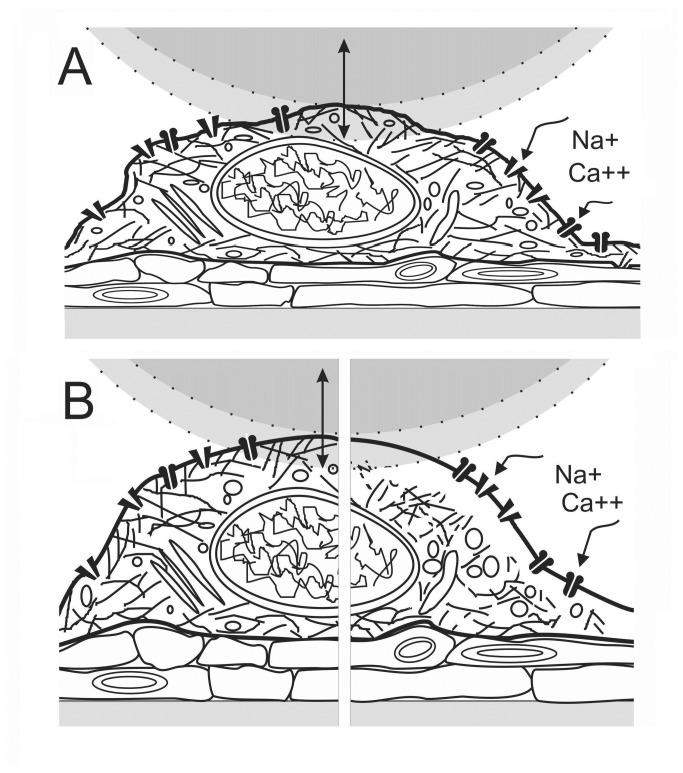
Figure 1. Cartoon of AFM force indentation measurements.
A. A neuron cultured with astrocytes is depicted approximately to scale against a 20 µm sphere whose maximum downward displacement during an indent excursion is shown shaded; force is measured during “down”. Cortical neuron excitotoxicity was mimicked using agonists for glutamate and Nav channels; NMDA opens NMDA-glutamate channels, dissipating the [Ca2+] and [Na+] gradients, whereas veratridine opens Nav channels, dissipating the [Na+] gradient. Neurons enlarge on exposure to hypotonic medium and to excitotoxic agonists. B. Our expectations for the state of an enlarged neuron in the presence of excitotoxic levels of agonist is depicted at early and later stages: at left, once the initial channel-mediated Na+ influx and osmotically-obligated H2O has hydrostatically inflated the neuron (countered to some extent by Ca2+-mediated actomyosin contractility), and at right, after Ca2+-toxicity has damaged the previously adherent (and contractile) neuronal membrane skeleton, allowing the plasma membrane to bleb pathologically.