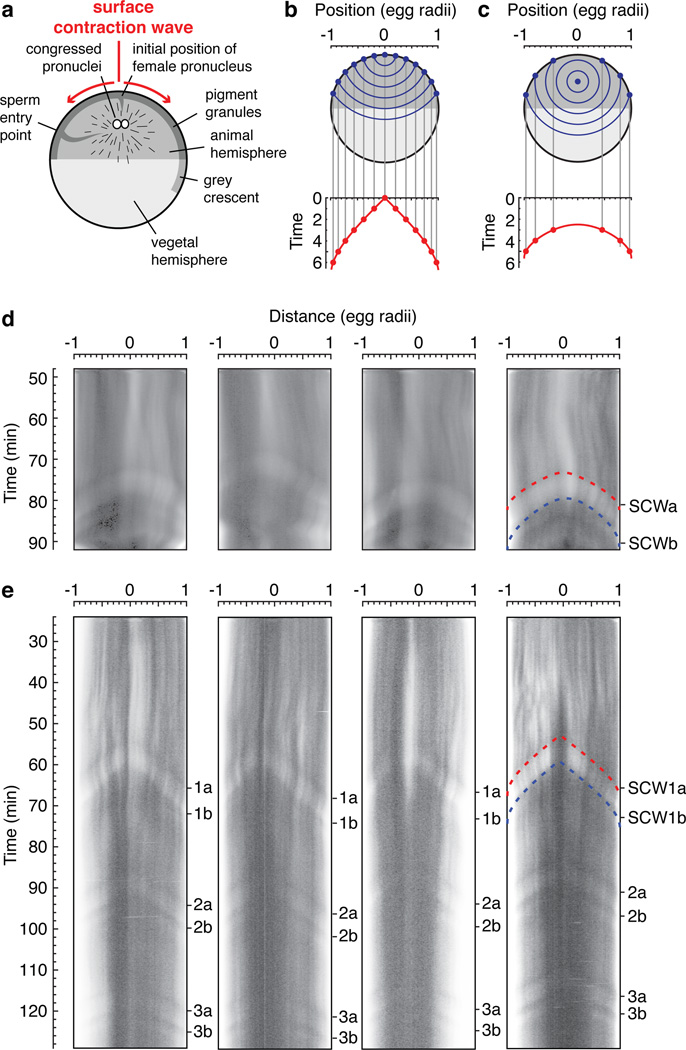
Figure 4. Surface contraction waves in intact Xenopus eggs.
a, Schematic view of the anatomy of a fertilized egg just before the onset of mitosis. Adapted from ref. 27. b, c, Expected propagation of surface contraction waves if they were due to a spherical wave of Cdk1 activation spreading from a point source. An equation for the spreading of the waves (Eq S1) is derived in the Supplementary Materials. Panel B assumes the point source is at the animal pole. Panel C assumes the point source is halfway between the animal pole and the center of the cell. d–e, Kymographs depicting surface contraction waves, indicated by transitions from light to dark or dark to light, in four fertilized eggs (d) and four parthenogenetically-activated eggs (e). The red and blue dashed curves are fits of the experimental data to the Eq S1. See also Supplementary Fig. 4.