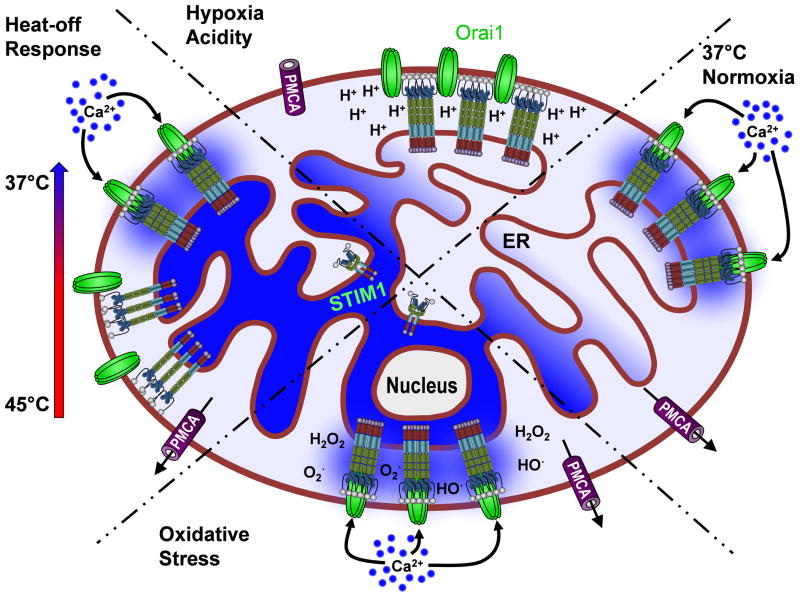
Figure 3. Multifaceted sensing strategies by STIM1.
RIGHT: Under normal physiological conditions, decreases in ER Ca2+ concentration lead to STIM oligomerization Orai channel activation and Ca2+ influx (Normoxia). TOP: Under hypoxic conditions, lack of ATP production prevents SERCA-mediated ER Ca2+ uptake, leading to decreased ER Ca2+ content. However, the concurrent accumulation of protons alters STIM/Orai coupling, preventing SOCE from occurring (Hypoxia/Acidity). BOTTOM: ROS overproduction promotes STIM activation of Orai by ROS-induced S-Glutathionylation of STIM, triggering store-independent Ca2+ influx (Oxidative Stress). LEFT: Increasing temperature causes a conformational change leading to oligomerization and clustering of STIM, without activation of Orai channels. Channels are activated upon cooling, due to the primed state of STIM and Ca2+ influx ensues (Heat-off Response).