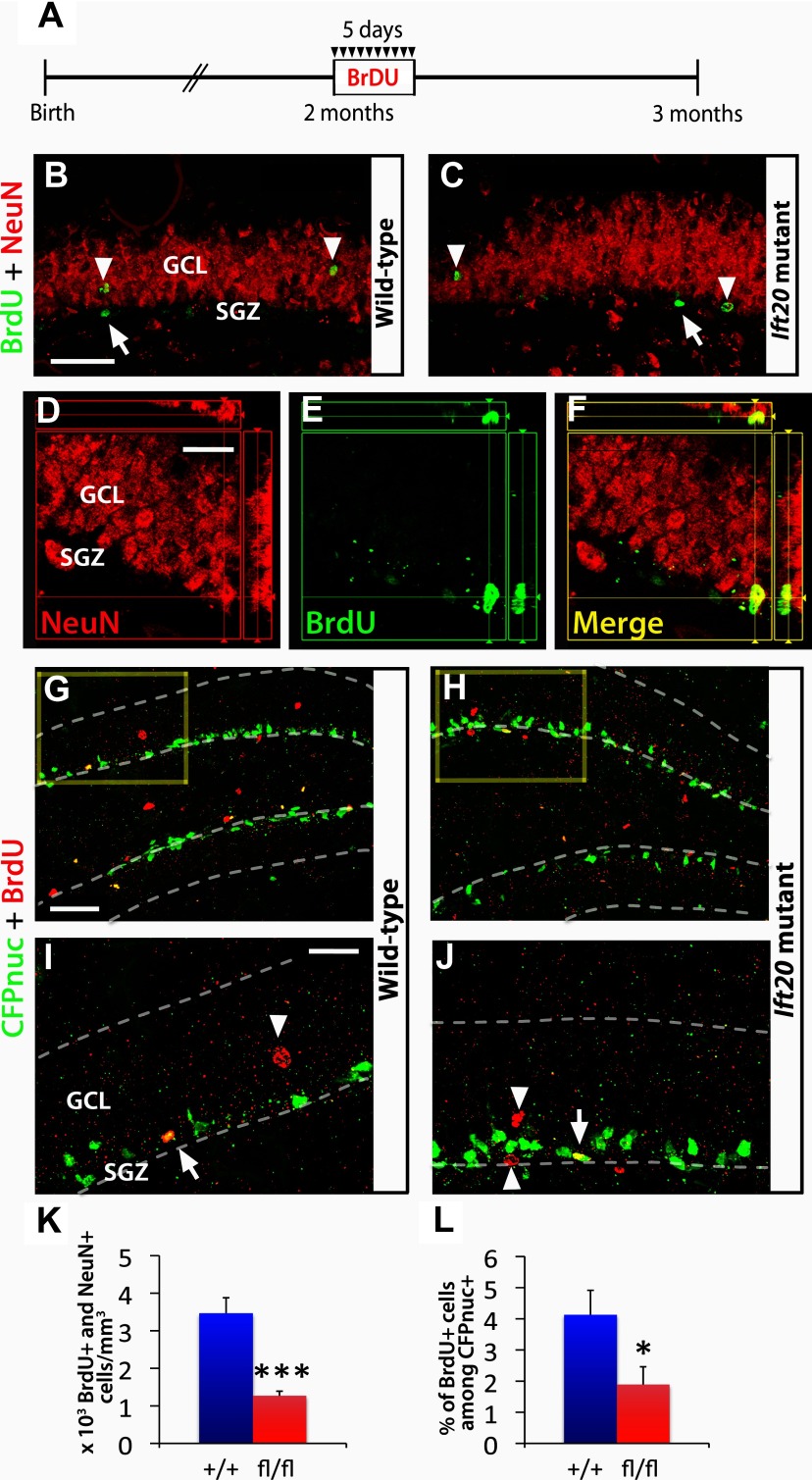
Figure 6.
Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is reduced in Ift20 mutant mice. A, A 5 d BrdU injection protocol (twice daily, 12 h apart, at 50 mg kg−1 body weight) was used in 8-week-old Ift20fl/fl::mGFAP-Cre (Ift20 mutant) and Ift20+/+::mGFAP-Cre (wild-type) mice, and the BrdU-labeled cells were examined 4 weeks after the last injection. B, C, BrdU (green) and NeuN (red) double staining 4 weeks after BrdU injection in Ift20 mutant and wild-type mice reveals BrdU-labeled adult newborn neurons (arrowheads; NeuN+) as well as other cell types in the SGZ (arrows; NeuN−). D–F, Colocalization of a BrdU+ (green) cell that coexpress the neuronal marker NeuN (red). G, H, CFPnuc (green) and BrdU (red) double staining, 4 weeks after BrdU injection, in 8-week-old Ift20fl/fl::mGFAP-Cre::nestin-CFPnuc (Ift20 mutant) and Ift20+/+::mGFAP-Cre::nestin-CFPnuc (wild-type) mice showing colocalization of BrdU+/CFPnuc+ cells along the SGZ. Higher magnification (squares) of G and H are displayed in I and J, respectively (arrows, BrdU+ stem/progenitor cells; arrowheads, other BrdU+ cells). K, Quantification of BrdU+/NeuN+ cells showed reduced neurogenesis in the GCL of the DG in Ift20 mutants compared with wild-type mice. L, Quantification of the percentage of BrdU+ among CFPnuc+ cells indicated reduced numbers of stem/progenitor cells that retained BrdU in Ift20 mutants compared with wild-type mice. Section thickness: B–J, 30 μm. Scale bars: B, C, 100 μm; D–F, I, J, 25 μm; G, H, 50 μm. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001. Data are expressed as mean values ± SEM.