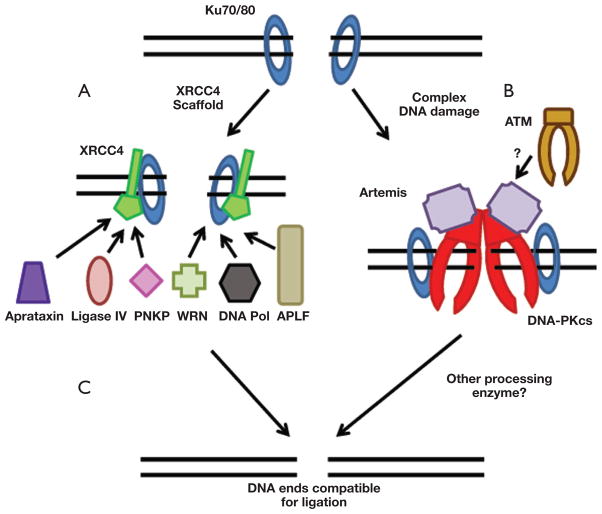
Figure 2.
DNA end processing. If required, a number of different processing enzymes can be utilized for making the DNA ends compatible for ligation for the terminal step of the NHEJ pathway; A. XRCC4, likely in conjunction with the Ku heterodimer, may serve as a scaffold required for the recruitment of specific DNA end processing enzymes. The XRCC4-Ku scaffold likely plays a role as a tool-belt where it can choose which enzyme is required depending on the nature of the DSB; B. Complex DNA damage may be processed via the DNA-PKcs-mediated recruitment of the nuclease Artemis and the processing of the complex damage may require ATM; C. Processing of the DNA ends makes them compatible for ligation