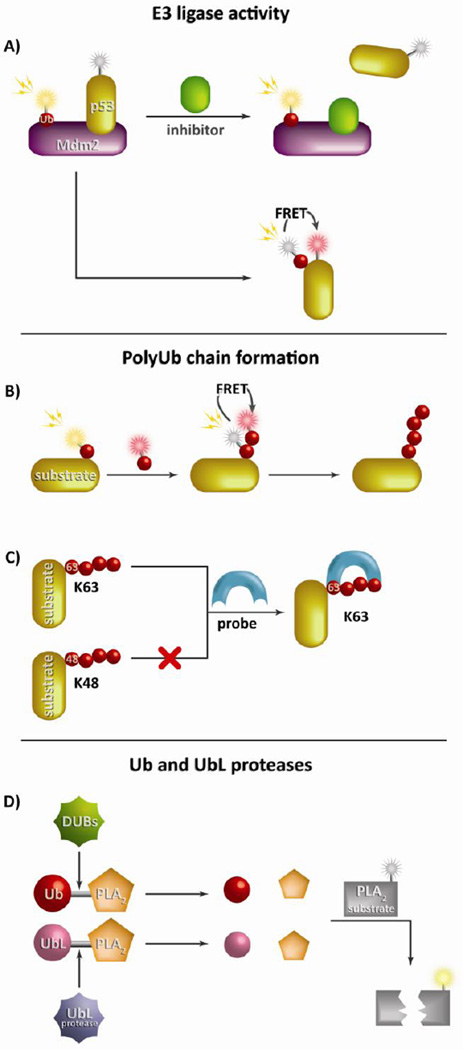
Figure 3. Measuring E3 ligase and DUB enzymatic activity and polyubiquitin chain formation.
Due to the complex nature of the ubiquitination enzymatic cascade, reporters have been developed to study a variety of key components. (A) A hallmark E3 ligase reporter was generated to monitor the interaction between p53 and its E3 ligase Mdm2 primarily using FRET pairings to evaluate substrate ubiquitination. This method is commonly employed in high throughput inhibitor screens. Reporters of polyUb chain formation can use multiple ubiquitin-conjugated fluorophores to detect chain formation by FRET (B) or specific binding domains to study precise lysine linkages such a K63 or linear polyUb chain formation (C). (D) The most common method to study Ub (or UbL) proteases such as DUBs employs Ub (or UbL) conjugated to the N-terminus of PLA2. Upon cleavage PLA2 is free is to cleave its substrate effectively liberating a detectable fluorophore.