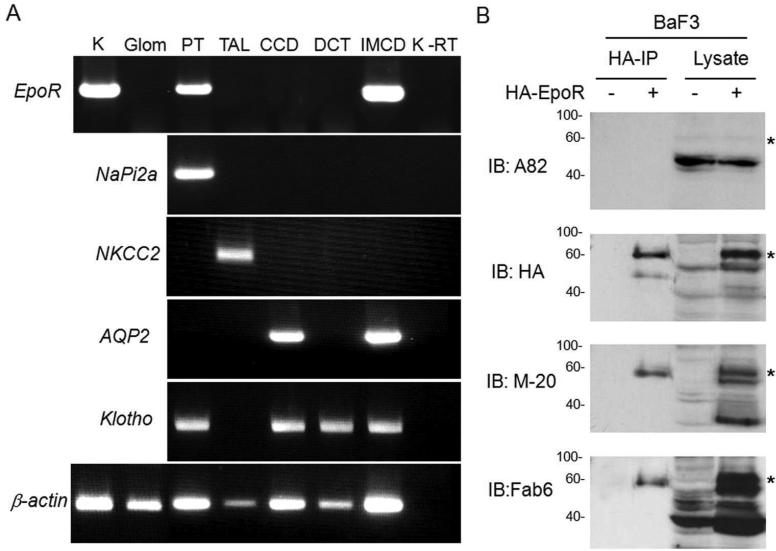
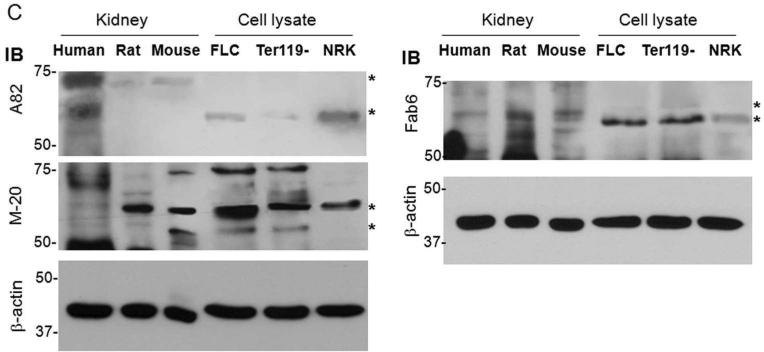
Figure 1. Expression of EpoR protein and mRNA in rat kidney.
(A) EpoR mRNA expression in the rat kidney or microdissected glomeruli and renal tubules and from normal adult rats at age of 3 months old by RT-PCT. Total RNA was extracted, and complimentary DNA (cDNA) generated with Oligo dT. Specific target genes were examined by PCR with rat specific primers (shown in method section). AQP2: aquaporin-2; CCD: cortical collecting duct; DCT: distal convaluted tubules; Glo: glomeruli; IMCD: inner medullary collecting duct; K: Rat kidney tissue containing cortex and medullar; NaPi-2a: Na-Pi dependent cotransporter-2a; NKCC2: Na-K-2Cl cotransporter; PT: proximal tubules; TAL: thick ascending limb; K-RT: kidney sample with reverse transcriptase omitted; (B) EpoR protein expression in BaF3 cell transfected with HA-tagged mouse EpoR or empty vector. Total lysates from native BaF3 and BaF3-HA-EpoR cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation by HA-Resin followed by immunobloting for EpoR with several anti-EpoR antibodies: A82, HA, M-20, Fab 6. Asterisks depict the specific HA-EpoR band. (C) Total proteins were extracted from human and rodent kidneys and murine FLC and Ter119-cells, and subjected to immunobloting EpoR with several antibodies against EpoR. A82 is monoclonal rabbit antibody kindly provided by Dr. Steve Elliot; M-20 is polyclonal antibody purchased from Santa Cruz Biotech. Fab 6 is a synthetic human Fab against human EpoR isolated from a phage-displayed library. Asterisks indicate multiple forms of glycosylated EpoR or EpoR fragments. Hu: human; Mu: mouse; FLC: fetal liver cells at E13.5