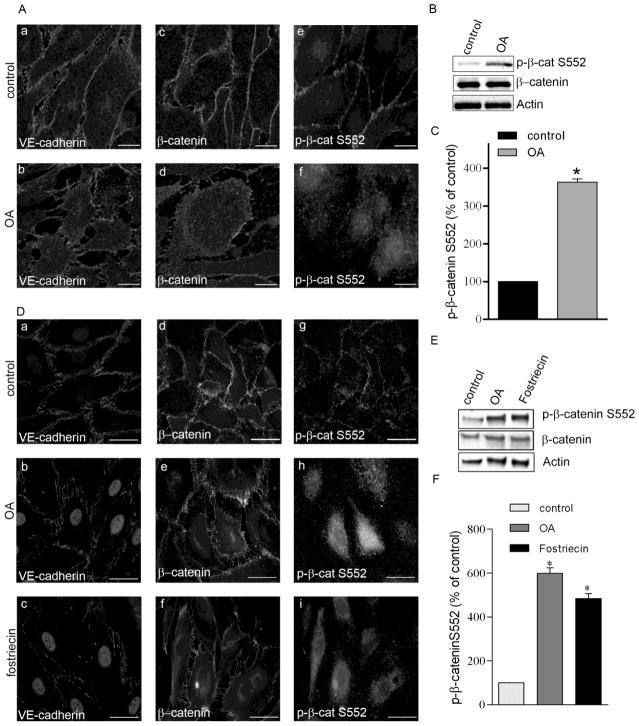
Figure 5. Okadaic acid and fostriecin treatment evokes redistribution of adherent junction proteins.
BPAEC (A,B) and HLMVEC (D,E) monolayers were treated with vehicle (Panel A: a,c,e; Panel D: a,d,g), 5 nM okadaic acid (OA) for 90 min (Panel A: b,d.f; Panel D:b,e,h), or with 100 nM fostriecin for 1 hr (Panel D: c,f,i). Afterwards the cells were fixed for immunofluorescent staining (A, D) or lysed for Western blot analysis (B,C) as described in Materials and Methods. Antibodies against VE-cadherin, β-catenin and phospho-β-catenin Ser552 were used as indicated in the immunofluorescent pictures to detect the subcellular distribution of adherent junction proteins. Pictures were taken with a Zeiss Axiolab microscope, scale bars: 200 μm. (B, E) Phosphorylation level of β-catenin on Ser552 was analyzed by Western blot using specific antibody against phospho-β-catenin Ser552. β-catenin and actin were also detected as loading controls. (C, F) Phosphorylation level of β-catenin was normalized to total β-catenin and quantified by densitometry of Western blots (n=3, p<0.05 vs control). Shown are representative data of three independent experiments.