Fig. 4.
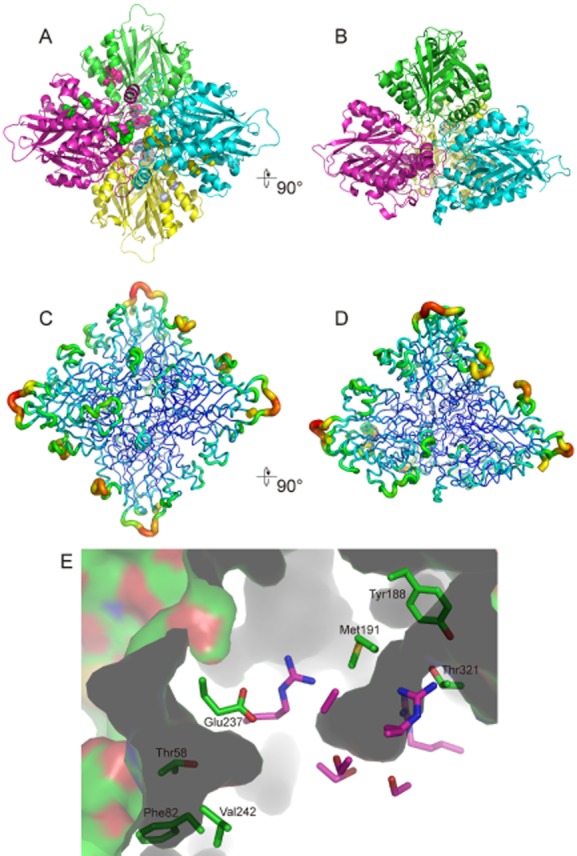
The AtzD tetramer.
A and B. Ribbon depictions of the tetrameric structure of AtzD and are approximate 90 degree rotations of each other. In (A) residues 58 and 81 (towards the periphery of the tetramer), and 188 and 191 (towards the centre of the tetramer) are shown as balls in colours that contrast with the main chain; these resides contribute to the two potential substrate channels.
C and D. The same rotations, but in this case the chains are coloured by B factors.
E. Two channels potentially provide access to the active site of each AtzD monomer. Active-site amino acid residues are shown in pink, but are otherwise unlabelled. The amino acid side-chains that form the channels are shown in green and their identities given.
