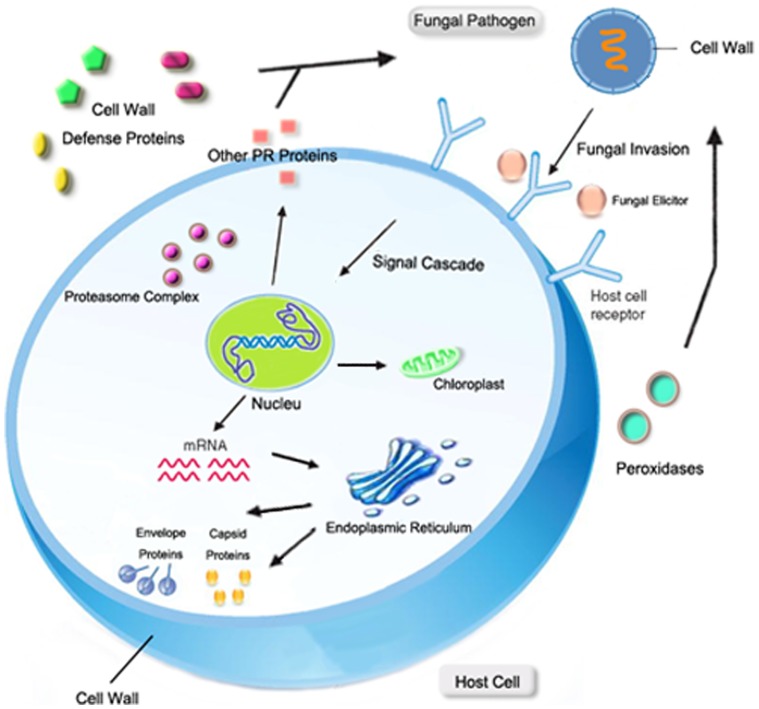
Figure 8. A hypothetical model representing the proteins involved in R. nigricans-tomato fruit interaction.
Pathogen invasion is perceived by the host plant that elicits defense responses in host plant by producing proteins that degrade fungal cell wall and to overcome accompanying oxidative stress. Cell death and heat shock response occurs to prevent disease development. The chloroplast elongation factor TuB (EF-TuB) is up regulated and Calvin cycle is damaged. Viral envelope proteins are induced at host cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Pathogen interaction enhances ethylene production that induces the ethylene-regulated responses in pathogen. Proteases located in cytoplasm, nucleus and proteasome complex are regulated in response to pathogen attack. Organelles showed in figure are involved in the interplay between pathogen and host plant.