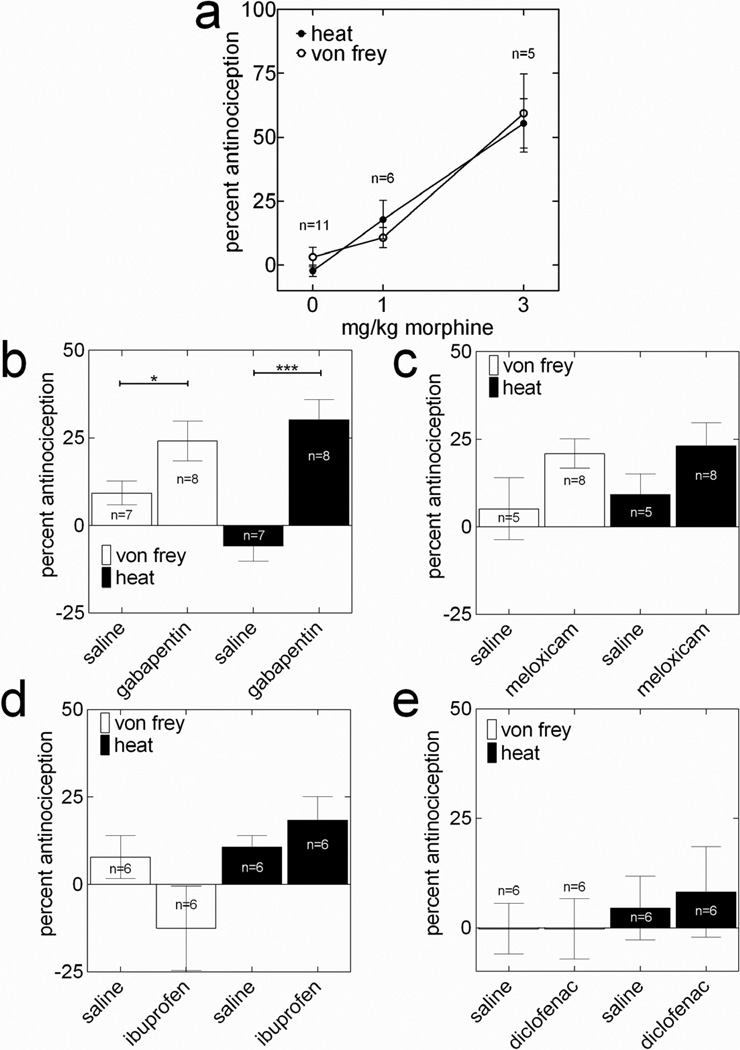
Figure 7.
PWT-H and PWT-M measures are identical in illustrating effects of analgesic compounds on recovery of incision-induced hyperalgesia. Two hours after incision, and on the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th postoperative days, rats were tested for baseline, and 30 min following blinded administrations of saline or morphine 1 or 3-mg/kg (a, PWT-H; F2,19=26.26 and PWT-M; F2,19=15.99, 1-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test), gabapentin (b, 50 mg/kg i.p.; *P<0.05, ***P<0.001, unpaired t-test; n=8), meloxicam (c, 10 mg/kg; i.p.; n=8), ibuprofen (d, 20 mg/kg i.p.; n=6), or diclofenac (d, 12 mg/kg; i.p.; n=6), on each respective day. Data are presented as mean±SEM of the percentage of maximum possible effect (%-MPE). See materials and methods for calculation of %-MPE values.