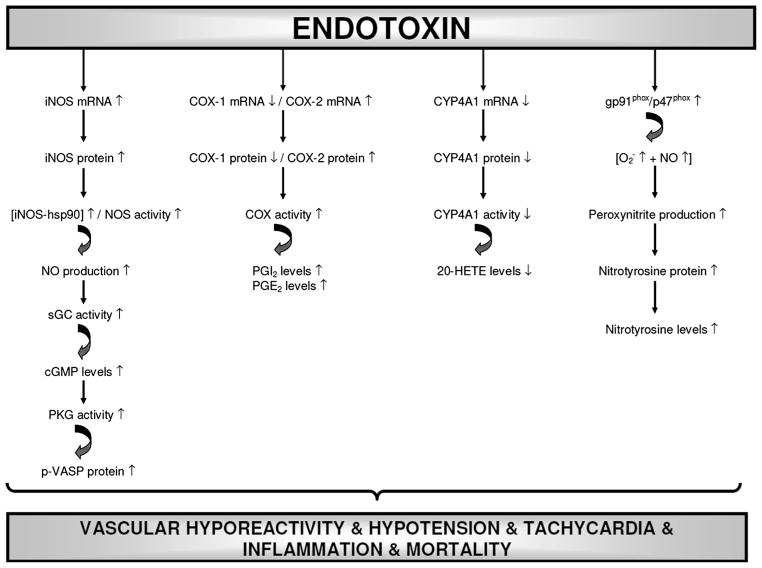
Fig. 21.
Schematic diagram showing the involvement of iNOS, sGC, PKG, COX-1, COX-2, CYP4A1, and gp91phox in endotoxin-induced vascular hyporeactivity, hypotension, tachycardia, and survival based on the results of the present and our previous findings. Endotoxin, the lipid A part of LPS which is the most potent microbial mediator of the pathogenesis of sepsis and septic shock, increases iNOS and COX-2 mRNA expression, iNOS, p-VASP, COX-2, gp91phox (NOX2; a superoxide generating NOX enzyme), p47phox (NOXO2; organizer subunit of gp91phox), and nitrotyrosine protein expression, iNOS-hsp90 complex formation, NOS activity, and levels of cGMP, 6-keto-PGF1α, PGE2, and nitrotyrosine associated with decreased COX-1 and CYP4A1 mRNA expression, COX-1 protein expression, and 20-HETE levels in renal and cardiovascular tissues leading to vascular hyporeactivity hypotension, tachycardia, and mortality in the rodent model of septic shock. 5,14-HEDGE, a 20-HETE mimetic, prevents the effects of endotoxin on the increase in expression of COX-1, COX-2, and CYP4A1 mRNA expression, iNOS, p-VASP, COX-2, CYP4A1, gp91phox, p47phox, and nitrotyrosine protein expression, iNOS-hsp90 complex formation, NOS activity, and levels of cGMP, 6-keto-PGF1α, PGE2, 20-HETE, and nitrotyrosine, and thus, restores blood pressure, prevents tachycardia, and improves survival during rodent endotoxemia. It should be noted that a competitive antagonist of vasoconstrictor effects of 20-HETE, 20-HEDE, prevents the effects of 5,14-HEDGE on blood pressure, HR, p-VASP, COX-2, CYP4A1, gp91phox, p47phox, and nitrotyrosine protein expression, iNOS-hsp90 complex formation, NOS activity, and 6-keto-PGF1α, PGE2, 20-HETE, and nitrotyrosine levels in rats treated with LPS. It can be concluded that decreased expression and activity of iNOS, sGC, PKG, COX-2, and gp91phox associated with increased CYP4A1 expression and activity participate in the protective effect of 5,14-HEDGE against vascular hyporeactivity, hypotension, tachycardia, and mortality in the rodent model of septic shock. (↑), increase; (↑) decrease.