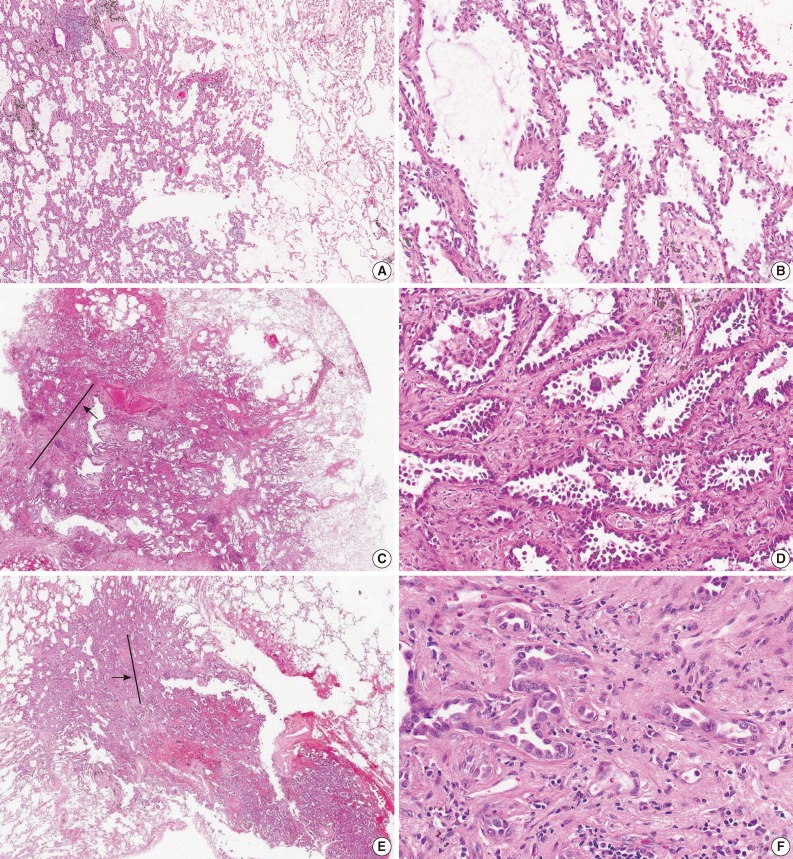
Fig. 1.
(A) Nonmucinous adenocarcinoma in situ. (B) Tumor shows continuous growth of neoplastic cells along the slightly thickened alveolar septa without disruption of the alveolar structures. (C) Equivocal invasion showing alveolar collapse. Tumor has a central scar (arrow) with a peripheral lepidic growth pattern. (D) The central scar demonstrates thick fibrous septa with intact tumor glands, but less identifiable alveolar architecture and plump, reactive fibroblasts. Some pathologists interpreted a desmoplastic stroma associated with tumor invasion, whereas others considered the same features as benign scarring/fibroelastosis in Thunnissen's reproducibility study.13 (E) Nonmucinous minimally invasive adenocarcinoma. Tumor consists predominantly of lepidic growth with a small invasion focus (arrow). (F) Tumor acini and single cells are invading in the desmoplastic stroma with chronic inflammatory cells.