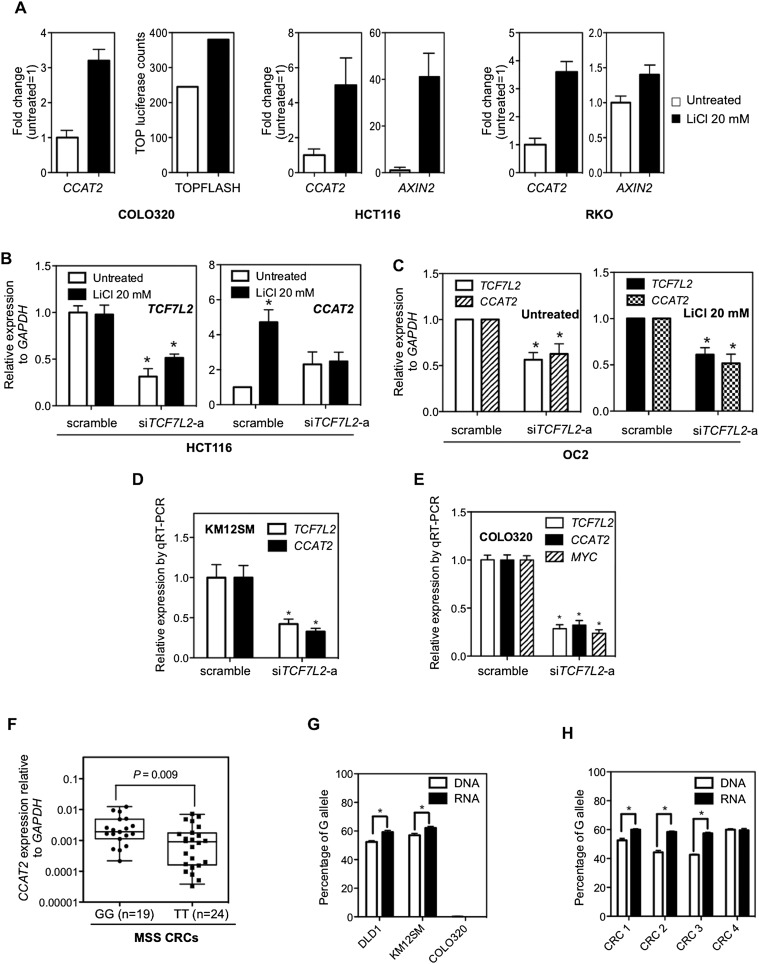
Figure 6.
Regulation of CCAT2 expression by WNT signaling and SNP variance on CCAT2 expression. (A) CCAT2 expression is induced by lithium chloride (LiCl) in three colon cancer cell lines. AXIN2 or TOP-Flash luciferase activity served as a positive control for the activation of WNT signaling. The data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). (B) TCF7L2 is indispensable for LiCl-induced CCAT2 expression. HCT116 cells were treated with TCF7L2 siRNA (siGENOME SMARTpool TCF7L2; Dharmacon) for 24 h and then stimulated with LiCl for another 24 h. CCAT2 expression levels were measured by qRT-PCR. (C) TCF7L2 siRNA down-regulates CCAT2 expression in overexpressing OC2 clone, either with or without LiCl stimulation. (D,E) TCF7L2 siRNA (sc43525, Santa Cruz) down-regulates CCAT2 expression in KM12SM cells and COLO320 cells. The data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3); (*) P < 0.05 when compared with the respective control. (F) Comparison of CCAT2 expression in cohort of CRC samples from Italy with GG and TT genotype showed higher CCAT2 expression associated with the G allele. The P-value was calculated using the Mann-Whitney test. The data are presented as box-whisker plots. (G,H) The Pyrosequencing data showed a higher percentage of the G allele in the CCAT2 transcripts than its genomic DNA counterpart in heterogeneous rs6983267 cell lines (DLD1 and KM12SM) and CRC patient samples with GT genotype. COLO320, which is TT genotype, served here as a negative control.