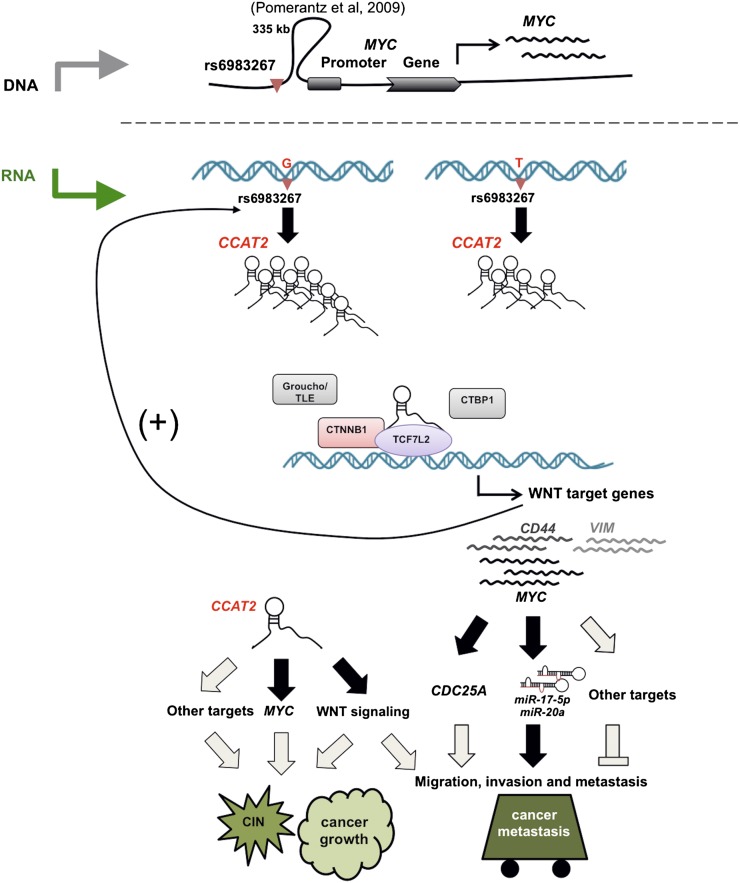
Figure 7.
A model of CCAT2 locus involvement in CRC. (Upper panel) An ∼335-kb DNA loop brings the rs6983267 genomic region close to the MYC locus, and this physical association may contribute to the enhancer function of the SNP-containing region on MYC transcription (Pomerantz et al. 2009). (Lower panel) The enhancer region is transcribed into a long noncoding RNA (CCAT2), and the SNP status affects CCAT2 expression by an as-yet-unknown mechanism. The CCAT2 transcript up-regulates WNT activity and increases expression levels of WNT target genes (including MYC). This regulation by CCAT2, possibly through its physical interaction with TCF7L2, may lead to genomic instability and promote cell growth. We demonstrated that MYC-regulated miR-17-5p and miR-20a participate in the CCAT2-enhanced cell invasion and speculate that other mechanisms, such as MYC-related mechanisms (CDC25A) or enhanced WNT signaling (VIM and CD44), may exist to coordinate the metastatic phenotype elicited by CCAT2. Finally, we demonstrated that CCAT2 expression is regulated by transcriptional factors TCF7L2, indicating a positive feedback loop between CCAT2 and WNT signaling. Our findings provide an additional explanation on the SNP-conferred CRC risk. (Black) Demonstrated; (gray) hypothesized interactions.