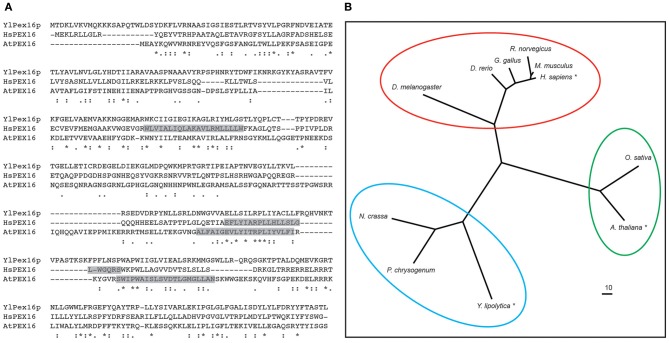
Figure 2.
Polypeptide sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis of various PEX16 proteins. (A) Deduced amino acid sequence alignment of Y. lipolytica Pex16p (YlPex16p), human (Homo sapiens) PEX16 (HsPEX16), and A. thaliana PEX16 (AtPEX16). Identical residues are indicated with asterisks, strongly and weakly similar residues are indicated with a colons and periods, respectively. Predicted membrane-spanning sequences in HsPEX16 and AtPEX16 are shaded and based on Honsho et al. (2002) and Karnik and Trelease (2007), respectively. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of PEX16 sequences from selected evolutionarily diverse species. Each protein is labeled based on its respective Genus and species, and those shown in (A) are indicated with an asterisk, and circles represent PEX16 proteins of the metazons, yeasts (fungi), and plants that form distinct clades. Branch lengths of the tree are proportional to divergence with the “10” scale bar representing a 10% change. Sequence alignments were carried out using either CLUSTALW (Larkin et al., 2007) and the phlyogram was generated using the program TreeView (v1.6.6). Genbank® accession numbers are as follows: H. sapiens (BAA88826.1), Rattus norvegicus (NP_001012088.1), Mus musculus (NP_660104.2), Drosophila melanogaster (NP_649252.1), Neurospora crassa (XP_963884.2), Danio rerio (NP_001020340.1), Gallus gallus (XP_421125.3), Penicillium chrysogenum (ABH11422.1), Y. lipolytica (AAB41724.1), A. thaliana (NP_566053.1), Oryza sativa (EEC72380.1).