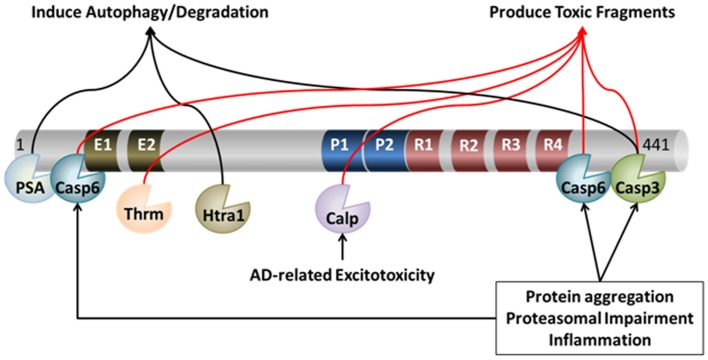
Figure 1.
Proteolytic processing of tau. Under pathological and physiological conditions, tau undergoes cleavage at many distinct proteolytic sites by a myriad of proteases. The action of these proteases can lead to both protection and/or exacerbation of pathology. For example, cleavage of tau by caspase (Casp) 3, caspase-6, calpain (Calp), and thrombin (Thrm) leads to the production of toxic fragments of tau that exacerbate pathology. On the other hand, cleavage of tau by PSA, Htra1, and – in some circumstances – caspase-3, may facilitate its degradation, which may protect neurons from AD-related neuronal death.