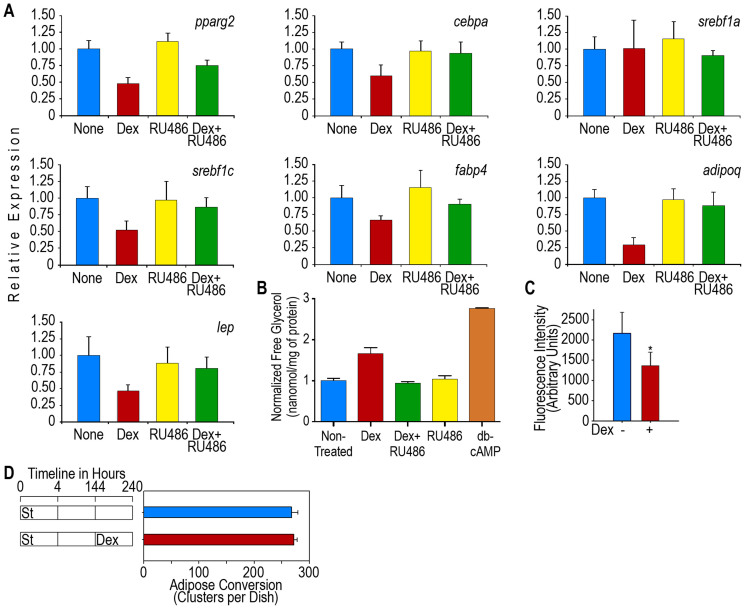
Figure 4. Dex impairs lipid homeostasis in mature 3T3-F442A adipocytes.
Adipose conversion in post-confluence 3T3-F442A cells was induced by St for 4 h. The cells were then transferred to non-adipogenic media for up to 144 h until the cells attained terminal differentiation. Then, cultures were treated with 0.25 μM Dex. (A). Expression of adipose genes in mature adipocytes. Mature adipocytes were treated for 24 h with Dex and data represent the mean fold change (compared to the gene expression in the absence of Dex) ± S.D. of 3 independent experiments (n = 9). All of the data were obtained at 168 h (24 h after Dex) except the adipoq expression data, which were obtained at 216 h (72 h after Dex). (B). Induction of lipolysis in mature adipocytes by Dex. Cultures of mature adipocytes were treated with Dex or the GR inhibitor RU486 or a mix Dex + RU486 and 24 h later free glycerol was quantitated. Cultures treated with db-cAMP were used as a lipolysis positive control. Results are presented as a mean ± S.D. of 2 independent experiments (n = 6). (C). Effect of Dex on the adipocyte uptake of NBDG. The 3T3-F442A adipocytes were cultured for 5 days in adipogenic medium with or without 0.25 μM Dex. The cells were incubated for 60 min with 80 μM NBDG and 100 mM insulin. After the 60-min incubation, the free NBDG was removed from the cultures, and the fluorescence associated with the cell monolayers was measured. The results are presented as the mean ± S.D. of 2 independent experiments (n = 16). (D). Effect of Dex on the number of adipose clusters after 3T3-F442A cell differentiation. Mature adipocytes were treated with Dex, then, cultures were followed for up to 96 h after Dex treatment and adipose clusters were counted. Data is presented as mean ± S.D. of 3 independent experiments (n = 9).