Figure 3.
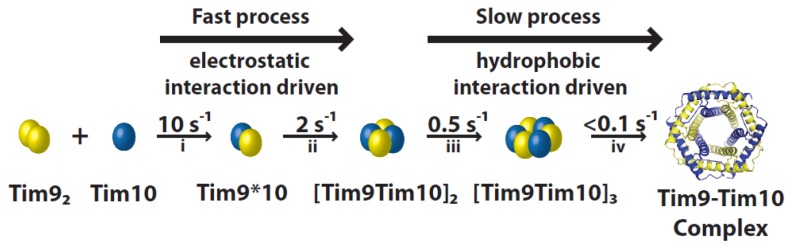
Tim9–Tim10 hexameric complex assembly. The process can be separated into four kinetic steps: formation of a heterodimer (i), a tetramer (ii), a hexamer (iii) and a final hydrophobic rearrangement (iv). The two initial fast steps are controlled mainly by electrostatic interactions, whereas the final two slow steps are driven by hydrophobic interactions.
