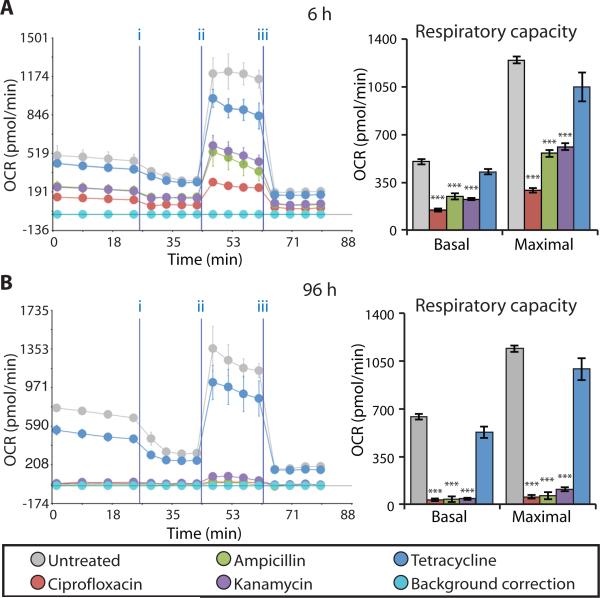
Figure 4. Bactericidal antibiotics decrease mitochondrial basal respiration and maximal respiratory capacity.
(A and B) Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was measured in MCF10A cells after 6 h (A) and 96 h (B) of bactericidal [ciprofloxacin (10 μg/ml), ampicillin (20 μg/ml), kanamycin (25 μg/ml)] or bacteriostatic [tetracycline, (10 μg/ml)] antibiotic treatment. Cells were treated with antibiotics followed by the Seahorse OCR protocol including treatment with three mitochondrial ETC complex inhibitors: (i) oligomycin, (ii) FCCP, and (iii) antimycin A. OCR measured before (i) represents basal respiration, while OCR measured between (ii) and (iii) represents the maximal respiratory capacity. Representative Seahorse OCR plots are shown and the bar graphs are means ± S.D. for n = 3. Comparisons between treatments and untreated controls were made using a Student's t test (***p < 0.001).