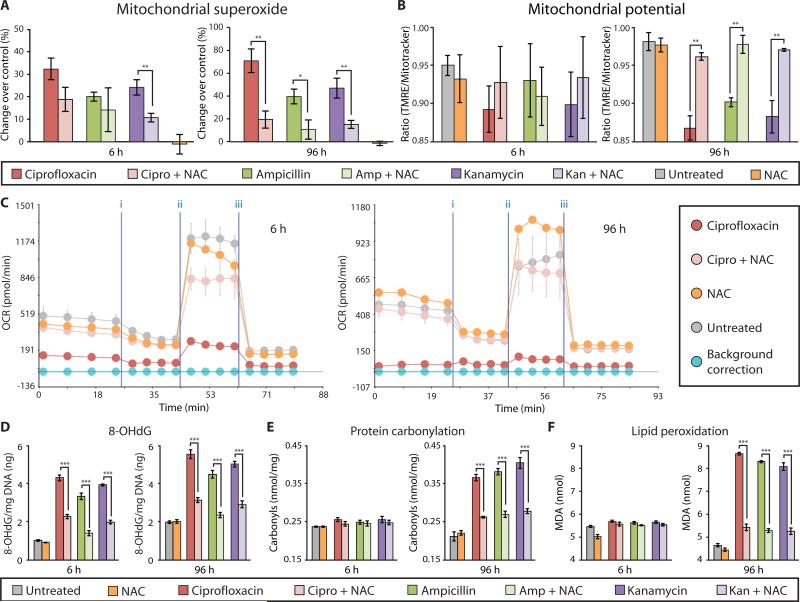
Figure 5. NAC rescues bactericidal antibiotic–induced oxidative damage in vitro.
MCF10A cells were incubated with and without NAC (10 mM) for 2 h, followed by treatment with ciprofloxacin (10 μg/ml), ampicillin (20 μg/ml), kanamycin (25 μg/ml), or tetracycline (10 μg/ml) for 6 and 96 h. (A) Mitochondrial superoxide was measured using MitoSox Red. (B) Mitochondrial membrane potential was quantified using TMRE and MitoTracker Green. (C) OCR was measured using the Seahorse XF24 flux analyzer, and a representative diagram testing the ciprofloxacin + NAC is shown. (See fig. S10 and S11 for ampicillin and kanamycin). (D) Oxidative DNA damage was assessed by quantification of 8-OHdG. (E) Protein carbonyls were quantified to evaluate oxidative protein damage. (F) Lipid peroxidation was measured by quantifying malondialdehyde (MDA). Data are means ± S.E.M. (n ≥ 3). Comparisons between treatment + NAC and treatments were made using a Student's t test (*p < 0.5, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).