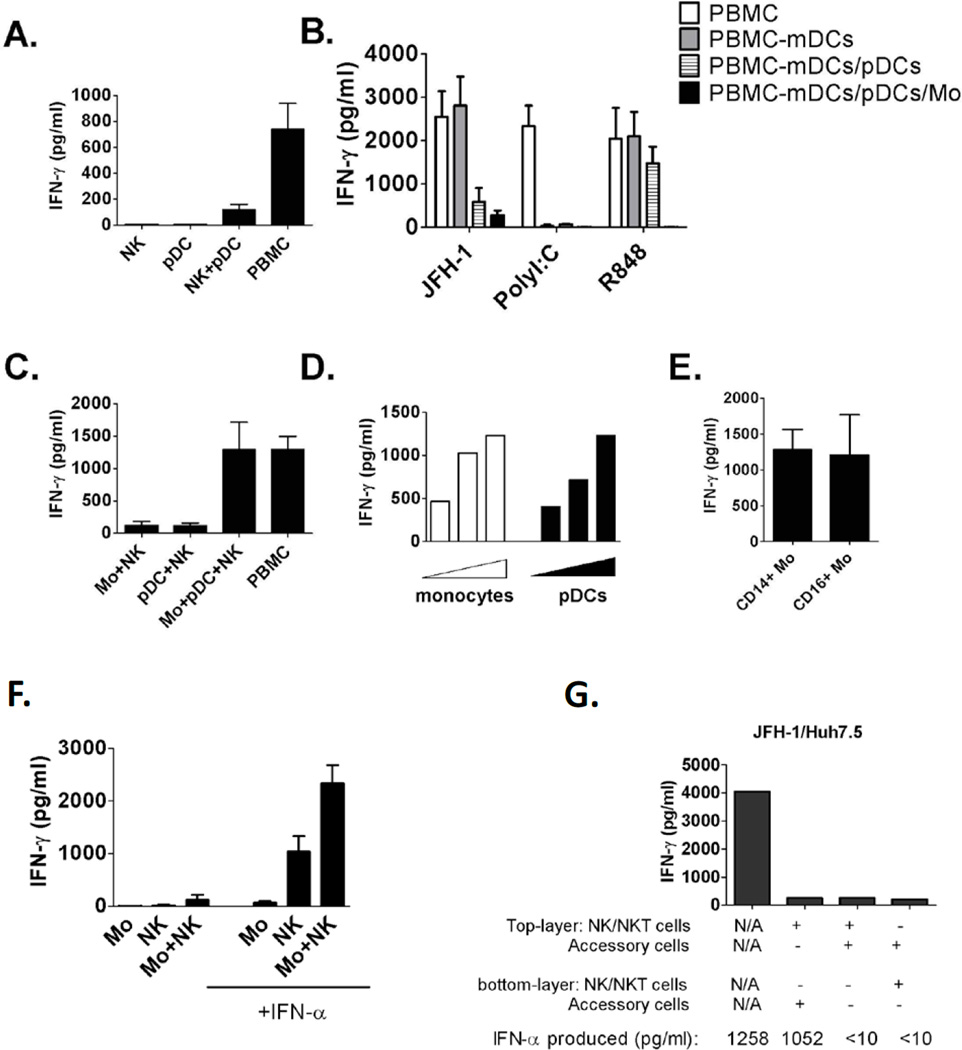
Figure 3. Both human pDC and monocytes are required for optimal IFN-γ induction in NK cells in response to HCV-infected cells.
(A) Purified human NK cells, pDCs, NKs and pDCs or PBMCs were co-cultured with JFH-1/Huh7.5cells for 24 hours. (B) Human PBMCs or PBMCs depleted of accessory cell subsets as indicated were co-cultured with JFH-1/Huh7.5cells for 24 hours. (C) Human monocytes, pDCs and NK cells were co-cultured with JFH-1/Huh7.5 cells for 24 hours. (D) Increased amounts of monocytes or pDCs were co-cultured with NKs and JFH-1/Huh7.5 cells for 24 hours. (E) Purified CD14+ or CD16+ monocytes were co-cultured with NKs and JFH1/Huh7.5cells for 24 hours. (F) Human monocytes and NK cells were co-cultured with JFH-1/Huh7.5 cells in the presence or absence of exogenous IFN-α for 24 hours. Data from (A–F) is represented as Mean±SD. (G) Accessory cells and NK cells were separated with co-cultured JFH-1/Huh7.5 cells using transwell insert as indicated, one representative data of three experiments was shown. In all experiments (A-G), IFN-γ production was measured by ELISA 24 hours after co-cultures.