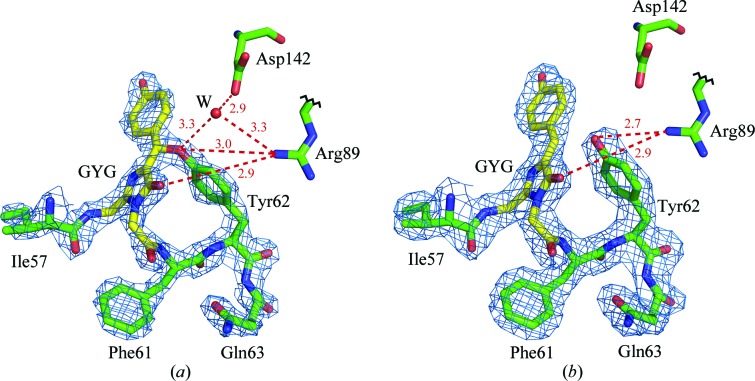
Figure 5.
The Gly58-Tyr59-Gly60 chromophore (GYG; shown in yellow) in 2F o − F c electron density: (a) laRFP (density cutoff ρ = 2.0σ) showing the presence of the covalent bond between the chromophore (Tyr59) Cβ and the proximal (Tyr62) O. The potential proton acceptor Asp142 forms a hydrogen bond (shown as a dashed red line), mediated by a water molecule (W), to the Tyr62 hydroxyl. The ligands of water W form a distorted tetrahedron and include another water molecule (not shown). Arg89 forms a hydrogen bond to the Tyr62 hydroxyl that presumably may facilitate proton transfer to Asp142. (b) laRFPdam (density cutoff ρ = 1.0σ) showing the absence of a covalent bond between the chromophore and Tyr62. No water molecule corresponding to W in LaRFP is present, most likely because of a 1 Å shift of the hydroxyl of Tyr62 towards Asp142. This figure was created with PyMOL (DeLano, 2002 ▶).