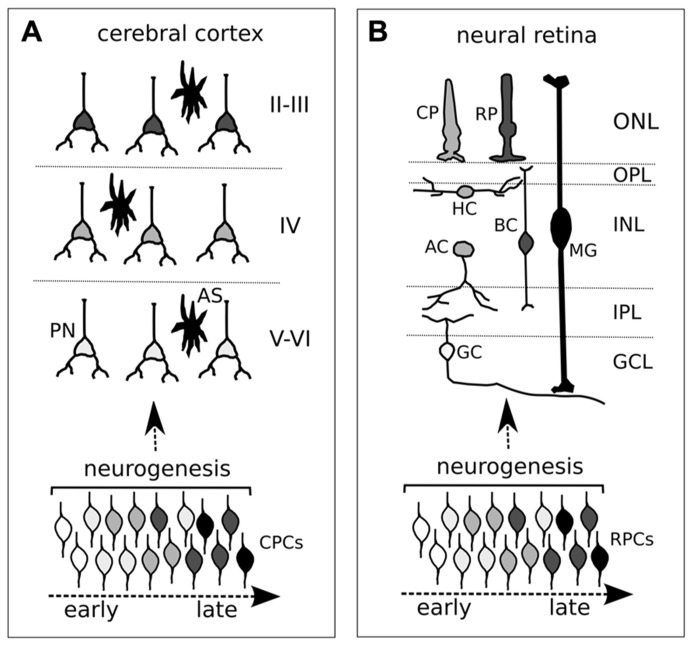
FIGURE 1.
Neurogenic timing in the developing cortex (A) and retina (B). (A,B) Different degrees of gray depict distinct neuronal identities in cortex (A) and retina (B). Both cortical and retinal progenitor cells (CPCs and RPCs, respectively) change competence over time (different degrees of gray from early to late). Although an overlap in neuronal cell birth periods is shown, the time of exit from the cell cycle (neurogenesis, or cell birth date) influences the acquisition of distinct cell identities of post-mitotic neurons. (A) CPCs comprise both ventricular (primary) and subventricular (secondary) progenitor cells. PN, projecting neuron; AS, astrocyte. Roman numerals indicate cortical layers. (B) Different retinal neurons and glia. CP, cone photoreceptor; RP, rod photoreceptor; HC, horizontal cell; BC, bipolar cell; MG, Müller glia; AC, amacrine cell; GC, ganglion cell; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer.