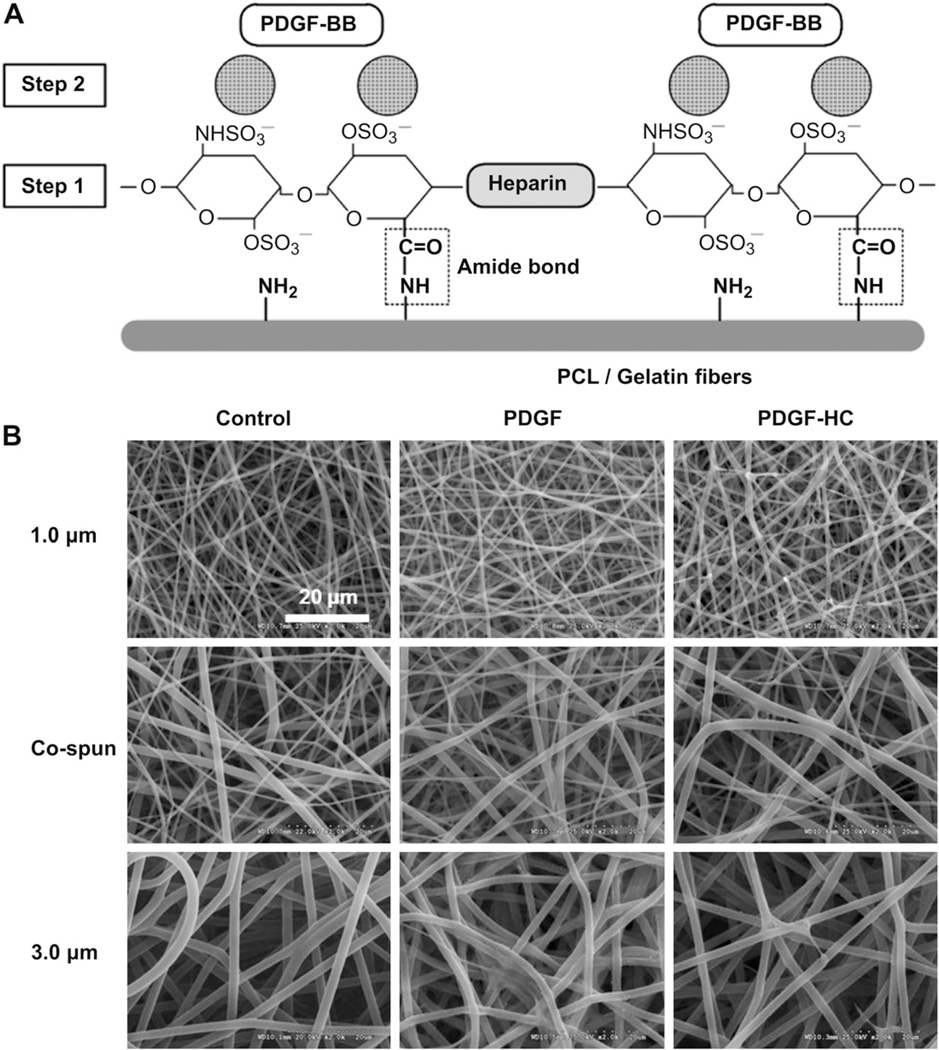
Fig. 1.
(A) Schematic diagram of PDGF-BB immobilization on heparin-conjugated electrospun PCL/gelatin fibers. [Step 1] heparin conjugation via the formation of amide bond. [Step 2] PDGF-BB immobilization through the electrostatic interaction between negative-charged heparin molecules and positive-charged PDGF-BB. (B) SEM images of (left column) electrospun PCL/gelatin fibers with three different fiber morphologies, (middle column) passive adsorption of PDGF-BB on the no heparin-conjugated fibers, and (right column) PDGF-BB immobilization on the heparin-conjugated fibers with a high affinity.