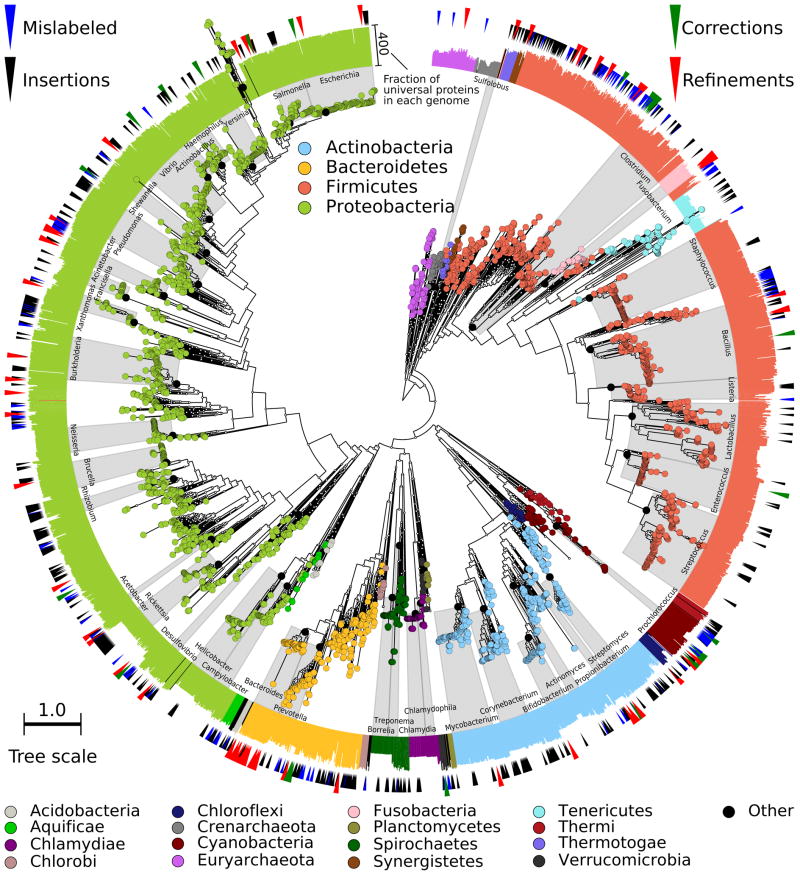
Figure 1. A high-resolution microbial tree of life with taxonomic annotations.
We reconstruct and validate a bacterial and archaeal phylogeny leveraging subsequences from 400 broadly-conserved proteins determined using 2,887 genomes and applied on a total of 3,737 genomes. The tree is built using RAxML28, with organisms colored based on phyla including at least 5 genomes. Scale indicates normalized fraction of total branch length. Gray labels indicate the lowest common ancestor of genera with at least 10 genomes (excluding predicted taxonomic mislabelings). External bar length represents the fraction of the 400 proteins contained in each genome. Red external triangles indicate genomes predicted by our method to be taxonomically mislabeled and confidently replaced; blue triangles indicate problematic labels that were refined but still did not fall within a fully consistent clade; green triangles indicate genomes whose incomplete taxonomic label we confidently refined; and black triangles indicate 566 genomes from IMG-GEBA that have been newly placed into the tree.