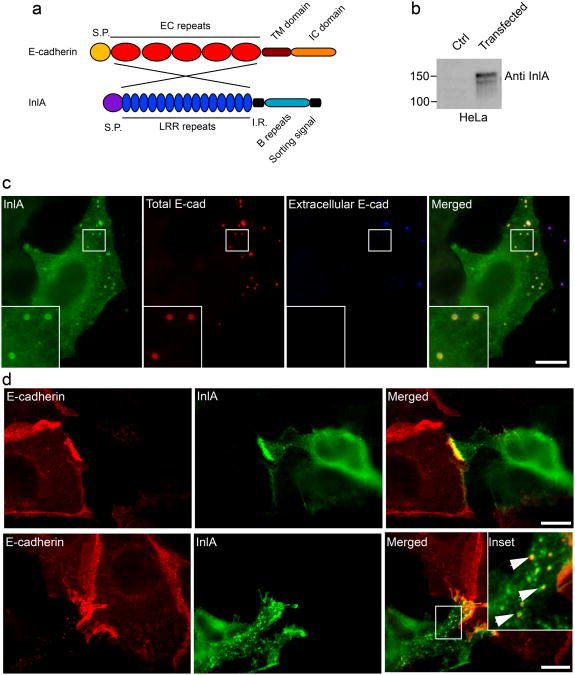
Figure 5.
InlA/E-cadherin interactions generate hybrid cell-cell junctions. a. The InlA/E-cadherin chimeric protein was generated by substituting the EC repeats of E-cadherin with the LRR repeats of the Listeria monocytogenes surface protein InlA. b. HeLa cells were transfected with a control plasmid or with a plasmid containing the chimeric DNA and the expression of the chimera was tested by Western blots with an InlA-specific antibody. c. HeLa cells transfected with the InlA-E-cadherin chimera were incubated with E-cadherin-coated beads for 1 h. Beads were labeled with an anti-E-cadherin antibody before (blue) and after permeabilization (red) to distinguish extracellular and intracellular beads and cells were labeled with an anti-InlA antibody (green) to detect transfected cells. d. HeLa cells transfected with the InlA/E-cadherin chimera were co-cultured with Jeg3 cells expressing endogenous E-cadherin. After an overnight incubation cells were fixed and labeled with an antibody against the extracellular domain of E-cadherin, that specifically recognizes endogenous E-cadherin (red), and with an InlA-specific antibody (green). When cell-cell contacts were more interdigitated we could observe the presence of endocytic vesicles positive for both InlA (green) and E-cadherin (red). Scale bars 10 μm.