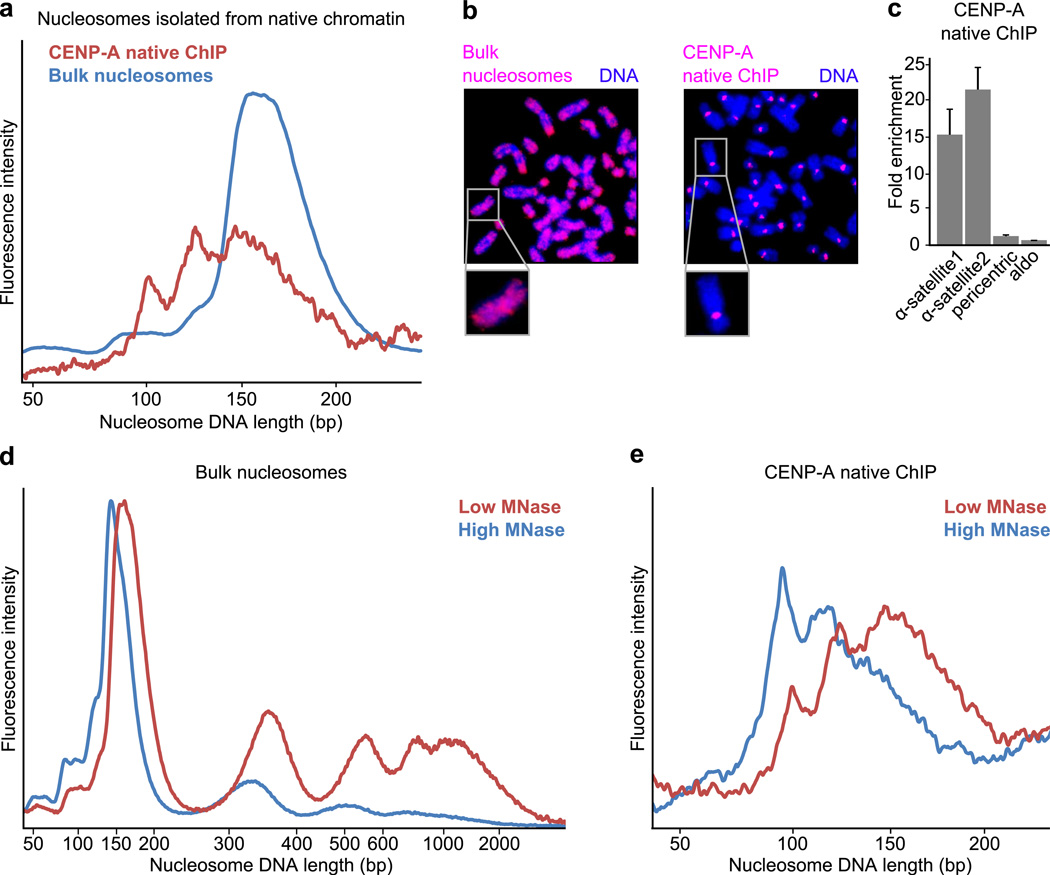
Figure 2. Nuclease digestion of native CENP-A-containing particles resembles that of octameric nucleosomes with loose termini.
(a) DNA length distributions of MNase-digested CENP-A native ChIP and bulk nucleosomes from the same preparation. (b) Fluorescence in situ hybridization using DNA from bulk nucleosomes or CENP-A native ChIP as probes. Bulk nucleosome DNA labels the entire chromosome whereas CENP-A probe labels solely centromeric regions, as expected. (c) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis comparing enrichment of CENP-A native ChIP DNA relative to bulk nucleosome DNA. CENP-A ChIP sequences are enriched for α-satellite regions (α-satellite1, α-satellite2), but not at pericentric or promoter (aldo) regions, as expected. Error bars represent s.e.m. from three independent replicates. (d) Standard digestion (red) or overdigestion (blue, threefold higher concentration of MNase used) of chromatin. (e) DNA length distributions of CENP-A native ChIP following standard digestion (red) or overdigestion (blue) of chromatin.