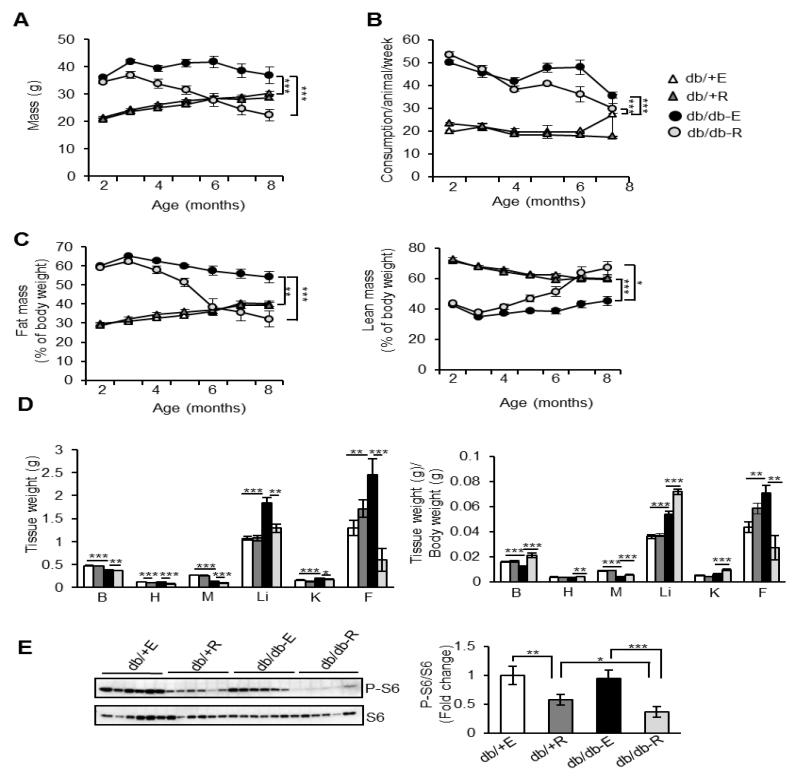
Fig. 1.
Rapamycin administration decreases fat accumulation in db/db mice. A) Body weights of non-diabetic control mice fed eudragit diet (db/+ E), non-diabetic control mice fed rapamycin diet (db/+ R), db/db mice fed eudragit diet (db/db-E) and db/db mice fed rapamycin diet (db/db-R) (n=9/group). B) Food consumption of db/+ E, db/+ R, db/db-E and db/db-R mice (n=9/group). C) Percentage lean mass and fat mass of db/+ E, db/+ R, db/db-E and db/db-R mice by QMR imaging. D) Tissue weights and weights of tissue normalized to body weight of db/+ E, db/+ R, db/db-E and db/db-R mice. B-brain, H-heart, M-skeletal muscle (gastroc), Li-liver, K-kidneys, F-gonadal fat. E) Left panel: Immunoblots of WAT extract from db/+ and db/db mice fed with eudragit or rapamycin with phospho-S6 (Ser 240/244; top panel) and total S6 protein (bottom panel). Right panel: quantification of phospho-protein to total protein. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.