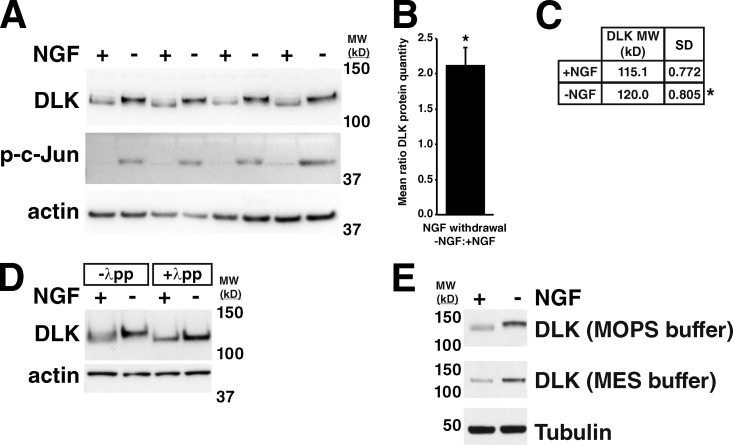
Figure 1.
DLK protein levels and molecular weight increase in response to NGF withdrawal from embryonic sensory neurons. (A) Increase in DLK abundance and molecular weight in response to NGF withdrawal from cultured embryonic DRGs. c-Jun phosphorylation (p-c-Jun) occurs as a downstream consequence of DLK and JNK activation. (B) Ratio of DLK protein quantity in −NGF vs. +NGF samples shown in A. Ratio = 2.12 ± 0.127. *, P = 0.02 by Mann-Whitney U test comparing the mean ratio to 1. Error bar represents SD. (C) Table showing molecular weight of DLK in kilodaltons (mean and SD) in +NGF and –NGF samples shown in A. *, P = 0.03 by Mann-Whitney U test comparing the molecular weights of DLK in the two conditions. (D) Lambda protein phosphatase (λpp) treatment of DRG lysates equalizes DLK molecular weight in −NGF and +NGF conditions. (E) Difference in mobility of DLK in SDS-PAGE with two different running buffers. MOPS buffer: SDS-PAGE running solution containing MOPS as a buffer. MES buffer: SDS-PAGE running solution containing MES as a buffer. MW (kD): molecular weight in kilodaltons.