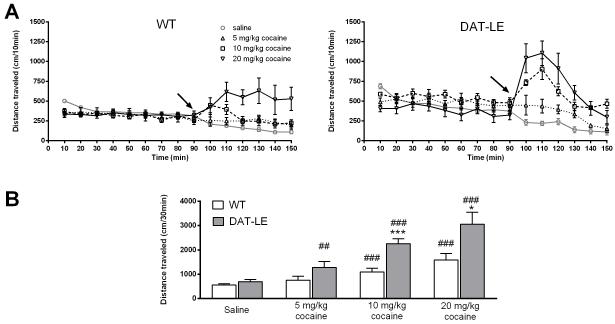
Fig. 4. Dose-effect of acute cocaine exposure on locomotor activity in DAT-LE and WT mice.
Following the 90-min habituation of the mice to the open field chamber on day 2 (see Fig. 3), WT (A, left panel) and DAT-LE (A right panel) mice were injected with a single dose of cocaine (arrow; 5, 10 or 20 mg/kg; mean values ± SEM, N = 6 for each dose and each genotype). Following injection, their locomotor activity was monitored for an additional 60 min. See Results for statistical analyses. Locomotor activity on day 1 following saline treatment is shown as a single group only for reference (N = 18). (B) Total distance traveled in the first 30 min after saline or cocaine injection (mean values ± SEM; * p<0.05, ***p<0.001, DAT-LE vs WT; ## p<0.01, ###p<0.001, cocaine vs saline within the respective genotype).