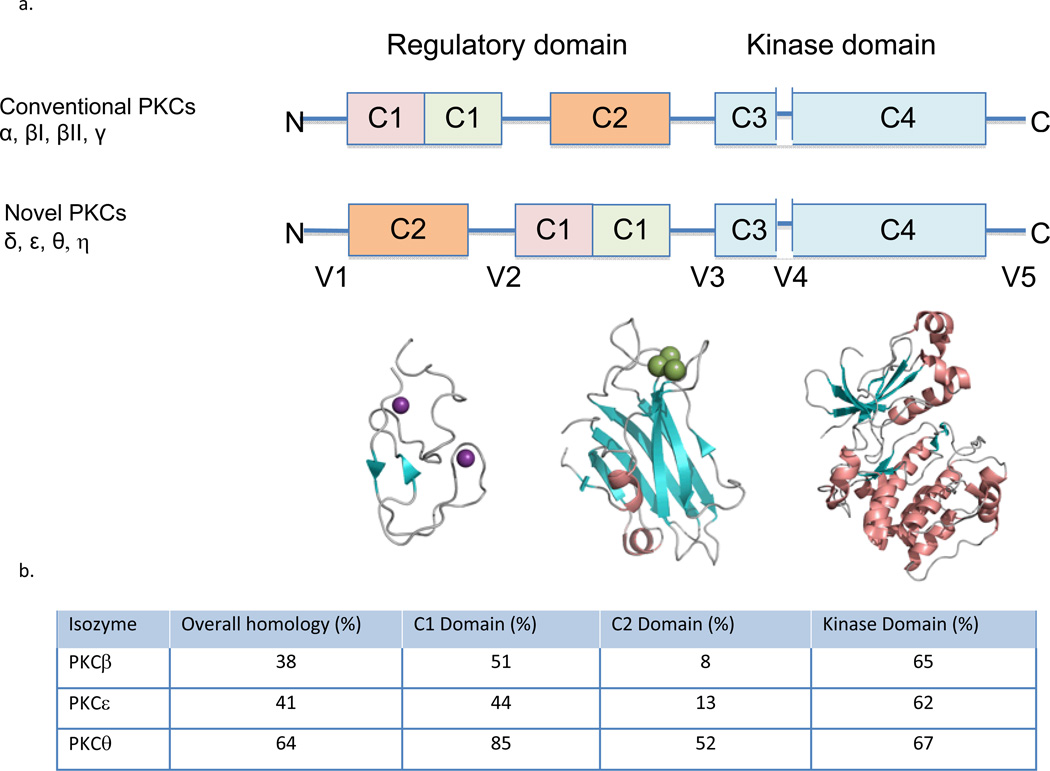
Figure 1.
a. Domain composition of PKC family members is shown in a stick scheme (not to scale). The structure of PKCβII (3PFQ) by domains; the diacylglycerol- binding C1a domain, the phosphatidylserine- (and calcium-) binding C2 domain, and the kinase domain. The secondary structures are α helix (in orange), β strands (in cyan) and loops (in gray), Zn2+ in purple and Ca2+ in green. b. The homology of different PKC isozymes to PKCδ. The C2 domain is the least conserved between the isozymes as compared with the other domains, suggesting that pharmacological tools that focus on the C2 domain are more likely to be isozyme-selective.