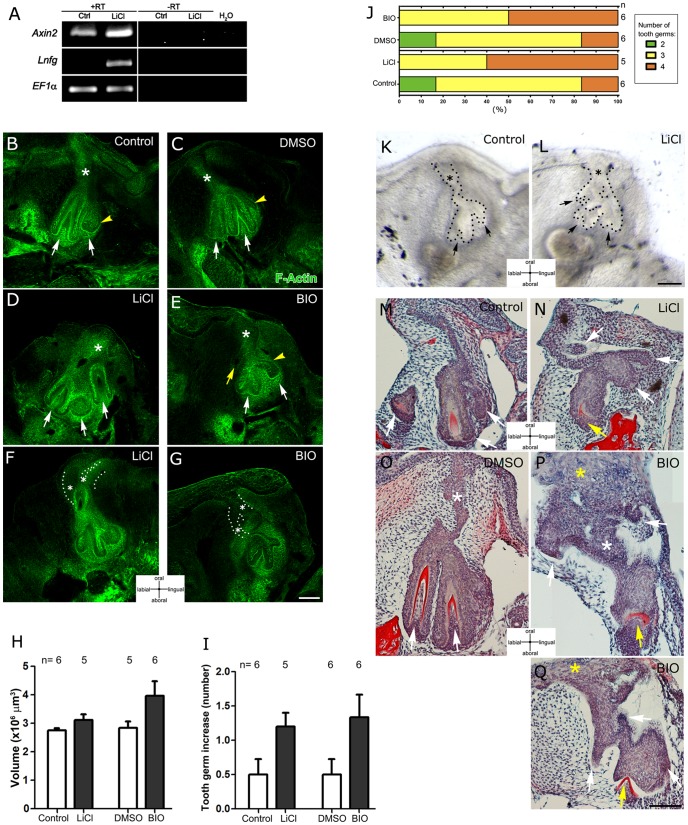
Figure 3. GSK3β inhibitors induce Wnt/β-catenin overactivation and increase the number of tooth germs in the snake.
(A) RT-PCR analysis of Axin2 and Lunatic fringe (Lnfg) mRNA levels of the dental organ indicating Axin2 and Lnfg are up-regulated after LiCl treatment. EF1α was used as a loading control. (B–G) F-Actin detection after 3 days of culture in (B) Control, (D,F) LiCl, (C) DMSO and (E,G) BIO. Asterisks: dental lamina, White arrows: tooth germs; yellow arrowhead: successional lamina. (H) The volume of the dental organ does not change after GSK3β inhibitor treatment. (I) Number of new tooth germs that appeared during 3 days of treatment and (J) percentage of the number of tooth germs in 3-day snake cultures after treatment, n = number of slices analyzed. (K,L) Morphology of dental organs after 7 days of control culture (K) and LiCl culture (L). Asterisks: dental lamina, Black arrows: tooth germs. (M–Q) Histology of explanted dental organs after 10 days in culture: (M) control, (N) LiCl treatment. (O) DMSO control and (P,Q) BIO treatment. White arrows: tooth germs and epithelial projections. Yellow arrow: dysmorphic tooth germ. White asterisks: dental lamina. Yellow asterisks: acanthosis in dental lamina. Scale bars: 100 µm.