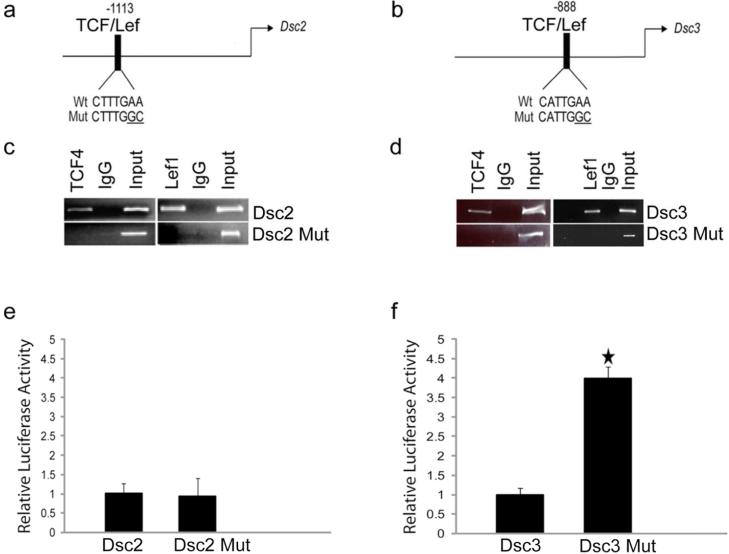
Figure 1. Identification and functional characterization of TCF/Lef factor-binding sites in the Dsc2 and Dsc3 promoters.
(a-b). Schematic representation of putative transcription factor binding sites in the proximal Dsc promoters. The arrows indicate translation start sites (ATG; A is defined as position +1). The DNA sequences of wild type (Wt) and mutant (Mut) transcription factor binding sites are shown. (c-d) ChIP assays demonstrating TCF/Lef binding to the predicted target sites in the Dsc promoters. Note that the point mutations introduced into the TCF/Lef target sequences (Dsc2 Mut, Dsc3 Mut) abrogate binding of the transcription factors. Input, chromatin used for immunoprecipitation; IgG, IP with unspecific IgG. (e-f) Reporter assays in mouse keratinocytes. Note that inactivation of the TCF/Lef binding sites in the Dsc3 construct increases reporter activity significantly. Error bars, standard deviation. Star indicates a statistically significant result (p-value < 0.05).