Figure 1.
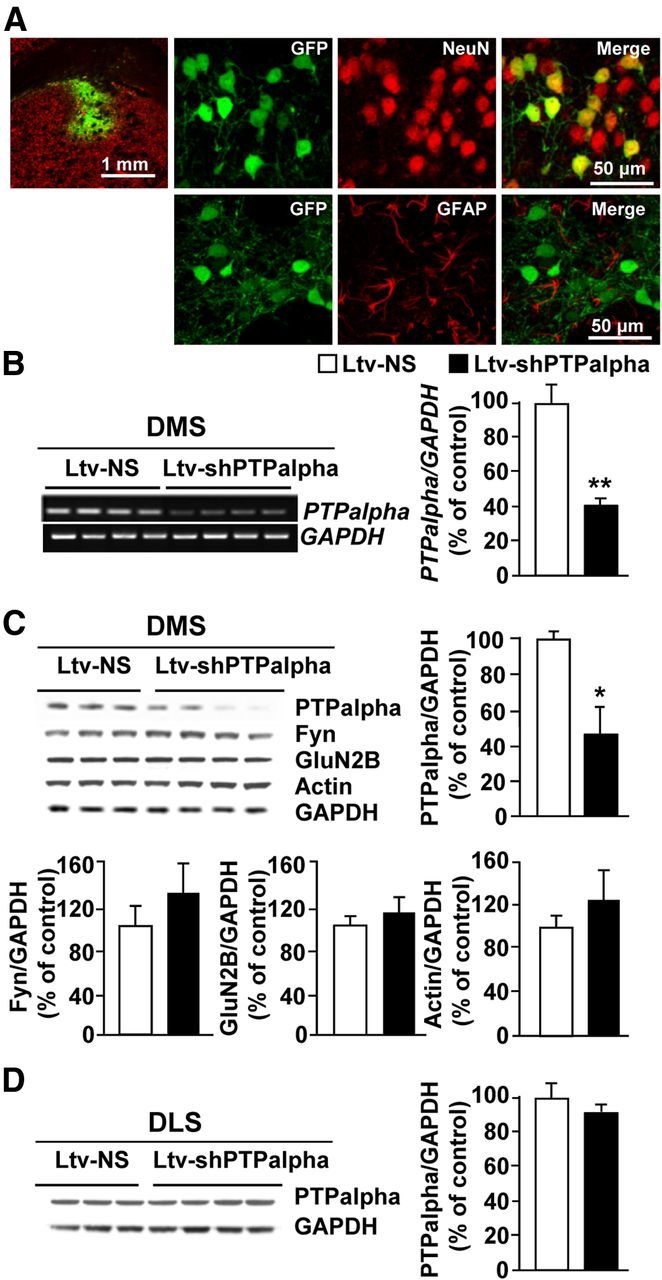
Infection of rat DMS neurons with a Ltv-shPTPα produces downregulation of the expression of the phosphatase. Recombinant Ltv-shPTPα or a Ltv-NS was bilaterally infused at a titer of 2 × 107 pg/ml into the DMS of rats. Striatal tissues were collected 6 weeks after virus infusions and used for immunohistochemistry (A), RT-PCR (B), and Western blot (C, D) analysis. A, Ltv-shPTPα infects DMS neurons. Top left, Specificity of the site of infection. Slices were costained with anti-GFP and anti-NeuN antibodies. Scale bar, 1 mm. Right, Costaining of GFP with NeuN (top) or GFAP (bottom). Scale bar, 50 μm. B–D, Ltv-shPTPα infection in the DMS decreases the mRNA (B) and protein levels (C) of PTPα in the DMS but not in the DLS (D). Ltv-shPTPα infection in the DMS does not change the protein levels of Fyn, GluN2B, or actin (C). GAPDH immunoreactivity was used as an internal loading control. Histograms represent the mean ratio of PTPα, Fyn, GluN2B, or actin/GAPDH ± SEM. Data are expressed as the percentage of control (Ltv-NS infected mice). *p < 0.05 (two-tailed unpaired t test). **p < 0.01 (two-tailed unpaired t test). B, n = 4. C, D, n = 3–4 for each group.
