Figure 10.
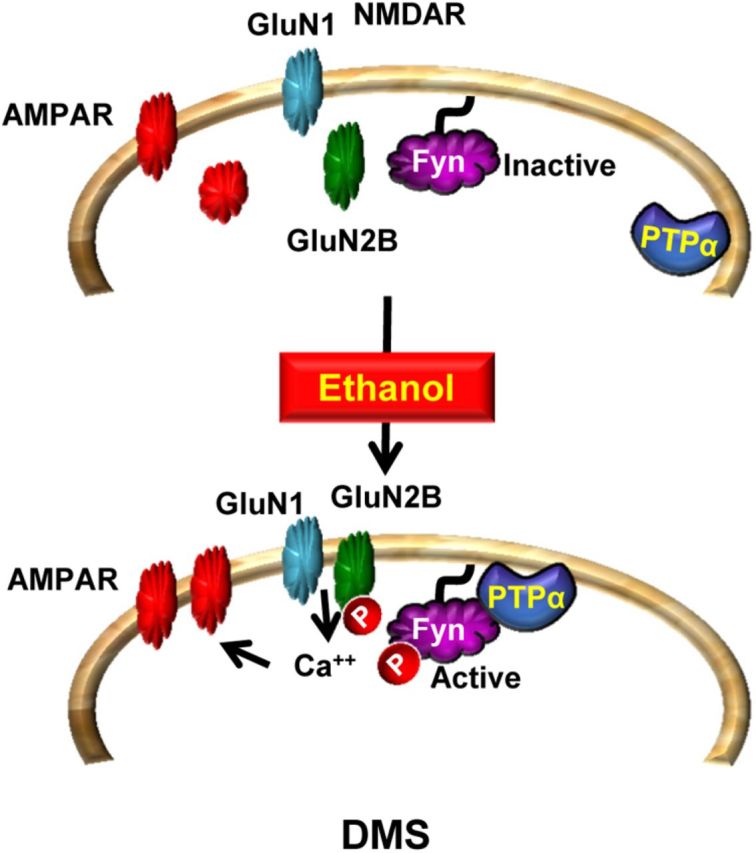
PTPα in the DMS of rodents promotes ethanol excessive drinking via Fyn. At resting state, PTPα is localized away from Fyn. Upon exposure of DMS neurons to ethanol, PTPα moves to the synaptosomal fraction where Fyn resides (Gibb et al., 2011; and herein). PTPα dephosphorylates the inhibitory site on Fyn, resulting in kinase activation. Fyn in turn phosphorylates GluN2B, leading to an increase in the synaptic membranal localization and activity of the channel (Wang et al., 2007, 2010, 2011). The sustained activation of NMDAR (Wang et al., 2007, 2010, 2011) leads to the movement of AMPARs to the synaptic membrane and to the enhancement of LTP (Wang et al., 2012). These plasticity events in the DMS promote excessive drinking of ethanol.
