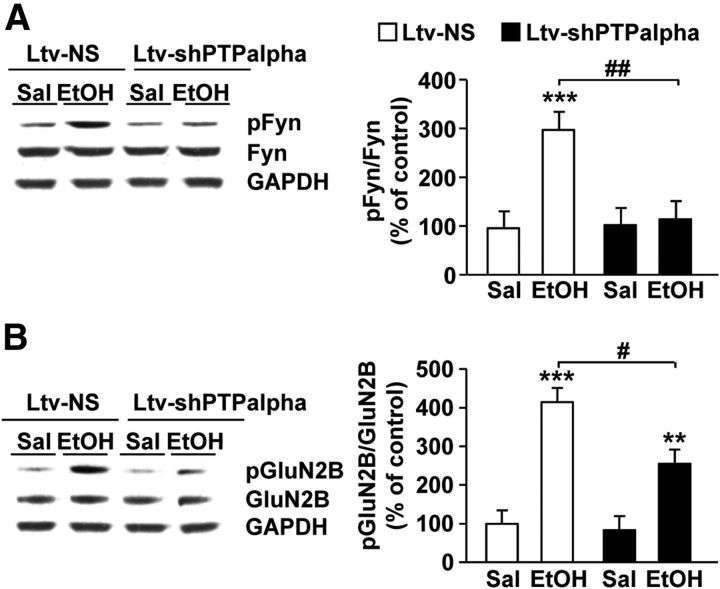
Figure 7.
PTPα knockdown in the DMS decreases ethanol-induced Fyn activation and GluN2B phosphorylation. Mice were infused with Ltv-NS or Ltv-shPTPα in the DMS. Four weeks after the virus infusion, animals were treated with an acute administration of saline (Sal) or ethanol (EtOH, 2.5 g/kg, i.p.) and the DMS was collected 15 min later. Anti-[pY418/420]Src/Fyn and anti-Fyn antibodies (A) and anti-[pY1472] GluN2B and anti-GluN2B antibodies (B) were used to detect the activated form and the total amount of Fyn (A) and the phosphorylated and total amount of GluN2B (B), respectively. Optical density of immunoreactivity of phosphorylated-protein bands was normalized to total protein and plotted as percentage of Ltv-NS/saline treatment. A, ***p < 0.001 versus Ltv-NS/Sal. ##p < 0.01 versus Ltv-NS/EtOH. B, **p < 0.01, versus Ltv-NS/Sal. ***p < 0.001 versus Ltv-NS/Sal. #p < 0.05 versus Ltv-NS/EtOH. n = 8 or 9 for each group.