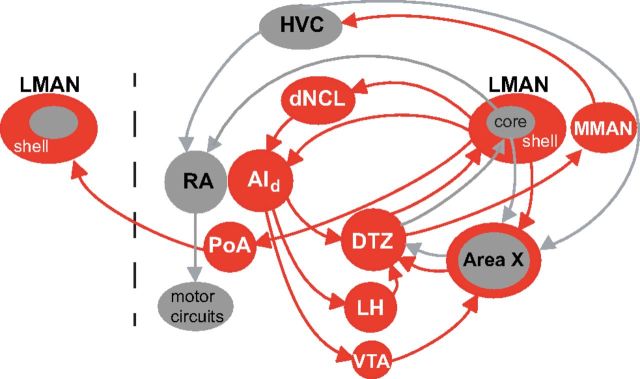
Figure 10.
Feedforward and feedback LMANshell pathways. Shell circuitry (red) contributes both to feedback pathways through thalamus and through integrative feedforward pathways. One feedforward pathway includes a projection from AId (previously referred to as Ad) to dopaminergic neurons in VTA and then to basal ganglia of the core pathway (Area X, gray). Feedforward pathways also project through a dorsal thalamic zone to MMAN and thence to HVC, which controls adult song production through its projection to vocal motor cortex (RA). Main feedback pathways include those discussed in the Results: shell → dNCL → AId → DTZ → shell and shell → Area Xshell → DTZ → shell. Additional recurrent loops may be made through the projection of AId to VTA and lateral hypothalamus. In addition, LMANshell projects to ipsilateral posterior amygdala, which sends axons to contralateral LMANshell, thereby constituting one pathway that could be used for interhemispheric coordination (Johnson et al., 1995). Posterior pallial amygdala was referred to as Av (ventral arcopallium) in previous papers from our laboratory, but we have changed the terminology here to conform to the nomenclature suggested by Reiner et al. (2004). Dashed line indicates midline. HVC, common name; RA, robust nucleus of arcopallium; dNCL, dorsal caudolateral nidopallium; AId, dorsal intermediate arcopallium; LMAN, lateral magnocellular nucleus of the anterior nidopallium; MMAN, medial magnocellular nucleus of the anterior nidopallium; DTZ, dorsal thalamic zone (includes DLM and DMP); Area X, basal ganglia nucleus containing both striatal and pallidal neurons; LH, lateral hypothalamus; VTA, ventral tegmental area; PoA, posterior pallial amygdala.