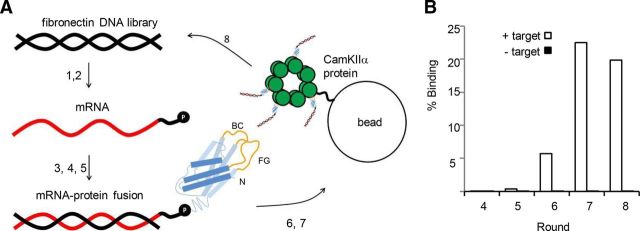
Figure 1.
mRNA display selection on CaMKIIα association domain. A, A round of selection consisting of (1) in vitro transcription of the fibronectin DNA library, (2) ligation of the resulting mRNA (red) to a DNA linker (black) fused to puromycin (P), (3) in vitro translation of mRNA and covalent linkage of fibronectin polypeptide (blue) to puromycin (randomized BC and FG loops in yellow), (4) oligo(dT) purification of mRNA-polypeptide fusions, (5) reverse transcription of mRNA to produce cDNA (black), (6) exposure of the mRNA/DNA-puromycin-polypeptide library to CaMKIIα association domain oligomers immobilized on agarose beads, (7) purification of mRNA/DNA-puromycin-polypeptides that bind at high affinity to CaMKIIα through affinity chromatography, and (8) PCR amplification of purified mRNA/DNA-puromycin-polypeptides to reconstitute a new DNA library of CaMKIIα-specific fibronectins. B, Percentage of mRNA/DNA-puromycin-polypeptides in Rounds 4–7 that bind to either CaMKIIα immobilized on agarose beads (+ target) or to beads alone (− target) in a hot binding assay. The percentage binding to target increases with later rounds, with negligible nonspecific binding.