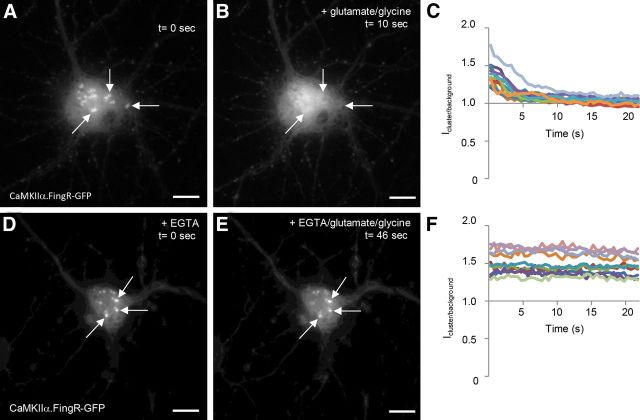
Figure 6.
CaMKIIα clusters rapidly disperse upon exposure to high concentrations of Ca2+. A, CaMKIIα.FingR-GFP labels clusters in the cell bodies of cortical neurons in culture. B, Ten seconds following the addition of 50 μm glutamate and 5 μm glycine, the clusters in A have disappeared. C, Time courses of the ratio of fluorescence of CaMKIIα.FingR-GFP at a point within a cluster versus at a point outside of the clusters (Icluster/background) for 10 different cells show that the clusters disappear at similar rates following exposure of cells to 50 μm glutamate and 5 μm glycine. D, Clusters labeled by CaMKIIα.FingR-GFP in cortical neurons in culture in the presence of 5 mm EGTA. E, Following exposure to 50 μm glutamate and 5 μm glycine for 46 s in the presence of 5 mm EGTA, the clusters in D do not change in shape or intensity. F, Time courses of Icluster/background for CaMKIIα.FingR-GFP in 10 different cells shows that clusters do not disperse when exposed to 50 μm glutamate and 5 μm glycine in the presence of 5 mm EGTA. Scale bars, 10 μm.