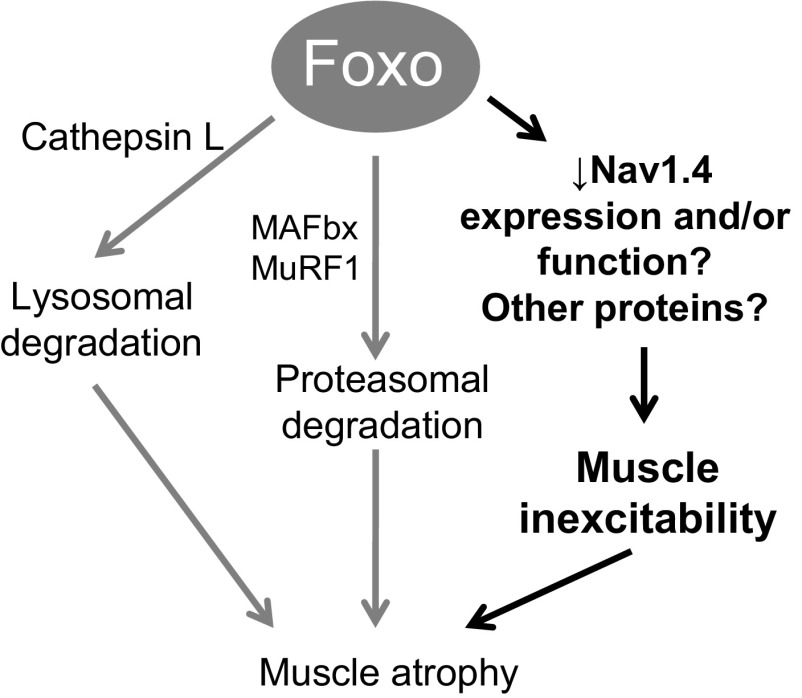
Fig. 9.
A working model that can account for the effects of Foxo1 on muscle excitability. Foxo1 regulates expression of proteins that carry out lysosomal degradation and proteasomal degradation leading to muscle atrophy. We here propose a novel mechanism in which Foxo1 transcriptional activity results in the inability of muscle fibers to respond to electrical stimulation. Foxo1 activity decreases the expression and/or function of sodium channel Nav1.4 and possibly other proteins critical for maintenance of excitability. Then, the lack of response to electrical stimulation and inability to contract, as seen in denervation and disuse, will eventually contribute to muscle atrophy.