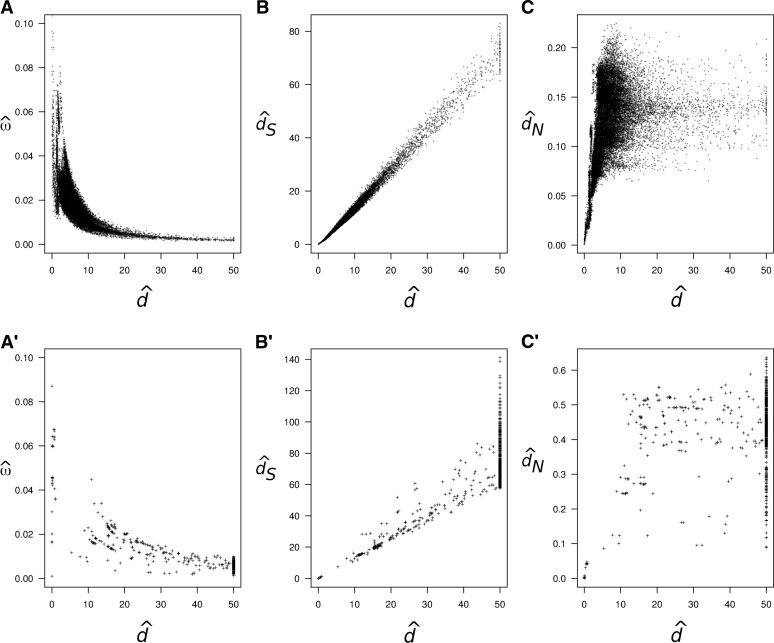
Figure 1.
Pairwise estimates of ω = dN/dS, d, dS, and dN for the mitochondrial protein-coding genes of placental mammals (A–C) and ribosomal protein-coding genes of bacteria (A′–C′). (A and A′) Pairwise estimates of ω vs. d. (B and B′) Pairwise estimates of dS vs. d. (C and C′) Pairwise estimates of dN vs. d. In A–C the estimates were obtained for all 29,646 comparisons among 244 mammal species, using the program CODEML from the PAML package (Yang 2007), with empirical codon frequencies and assuming no ω variation among sites. The estimates obtained from a joint analysis of all species on the phylogeny are and . The alignment of 244 sequences is 3598 codons long, but only 3411 codons are used after removing alignment gaps. In A′–C′ the estimates were obtained for all 1176 comparisons among 49 bacteria species as for the mammal case. The estimates from the joint analysis are and . The alignment is 4324 codons long (1968 codons after removing alignment gaps). The mitochondrial protein-coding genes and the ribosomal protein-coding genes (rplA-rplF and rplI-rplT) were obtained from GenBank.