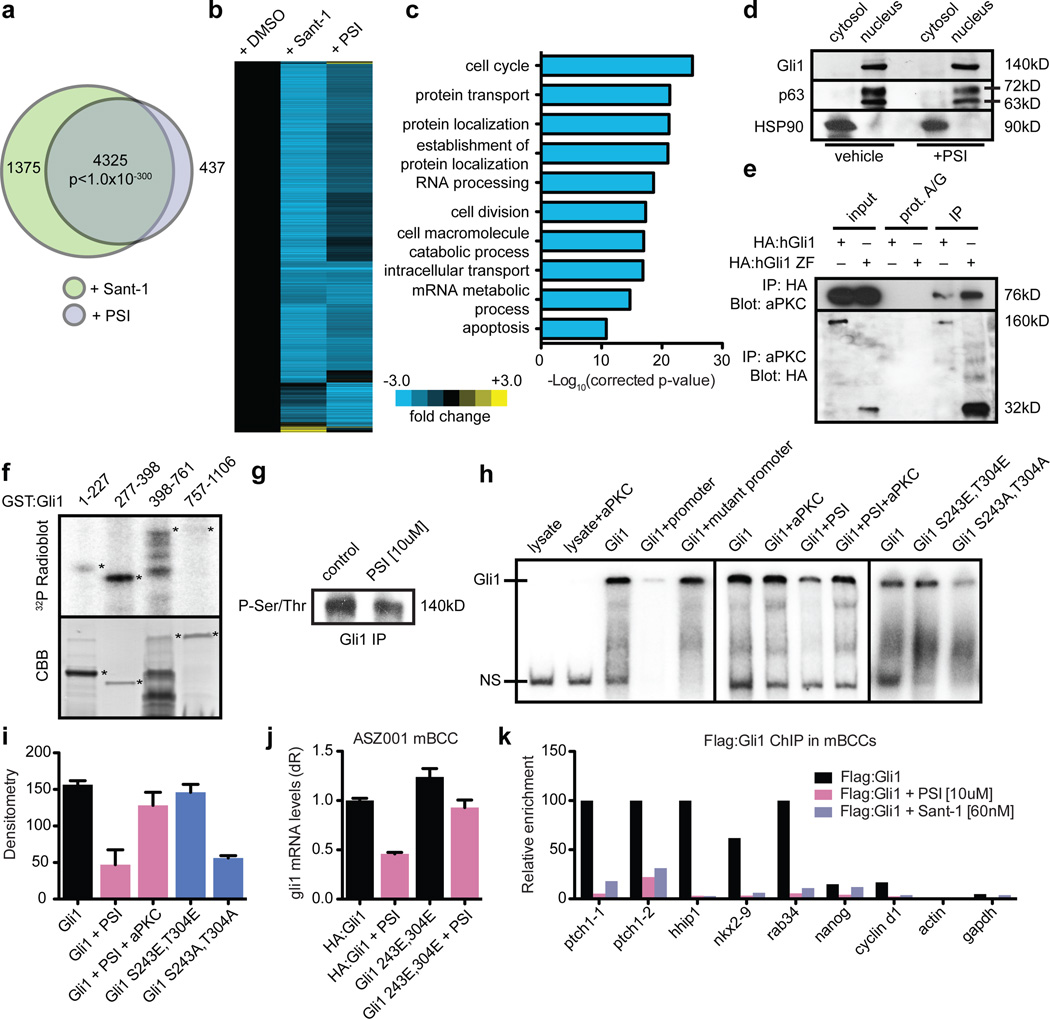
Figure 3. aPKC phosphorylates and activates Gli1.
a, Venn diagram and (b) heatmap of significantly changed transcripts upon Sant-1 or PSI treatment in BCC cells. c, Gene ontology terms of commonly altered transcripts. d, PSI does not affect nuclear Gli1 in BCC cells. e, aPKC interacts with in vitro translated (IVT) human Gli1 or Gli1 DNA-binding domain. f, aPKC phosphorylates human Gli1 DNA-binding domain. CBB, coomassie brilliant blue. g, PSI reduces phosphorylated serine/threonine levels of immunoprecipitated Gli1 from BCC cells. h, aPKC promotes DNA binding of IVT human Gli1 at S243 and T304 in an electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). NS, non-specific binding. i, Densitometry of aPKC rescue, phosphomimetic versus phosphodeficient Gli1 EMSA (n=3). j, BCC cells expressing phosphomimetic Gli1 show reduced PSI sensitivity (n=3). Error bars, s.e.m. k, Flag:Gli1 ChIP showing PSI and Sant-1 inhibit Gli1 binding to target chromatin sites in mouse BCC cells.