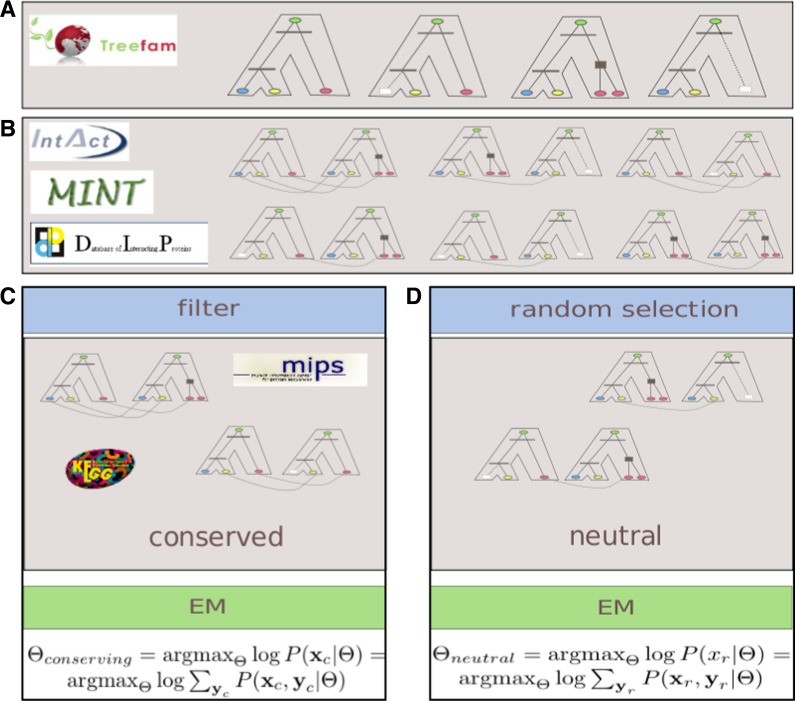
FIG. 1.
Estimating the parameters of conserving and neutral evolution of protein interaction networks: (A) Phylogenetic trees representing the evolution of specific protein families marked with duplication (filled box) and speciation (horizontal line) events are downloaded from the TreeFam database. The trees are pruned to consider only the seven species of interest. (B) Protein–protein interactions are downloaded from three major databases and are associated with the corresponding proteins in the leaves of the phylogenetic trees. Only pairs of trees for which there exist at least one interaction between member proteins are collected. (C) A filter is applied to the available pairs of trees to select for the conserved training set of pairs of families in which member proteins coexist either in the same KEGG pathway or a MIPS complex. (D) The second training set is comprised of an equal number of randomly selected pairs of trees. The model parameters for the conserving evolution scenario are estimated using the EM procedure based on the evidence from the conserved training set. The parameters for the neutral evolution scenario are derived based on evidence from the random set. Subsequently, the two estimated sets of model parameters are used to classify interactions between a new pair of protein families as either conserved or evolving under the neutral scenario.