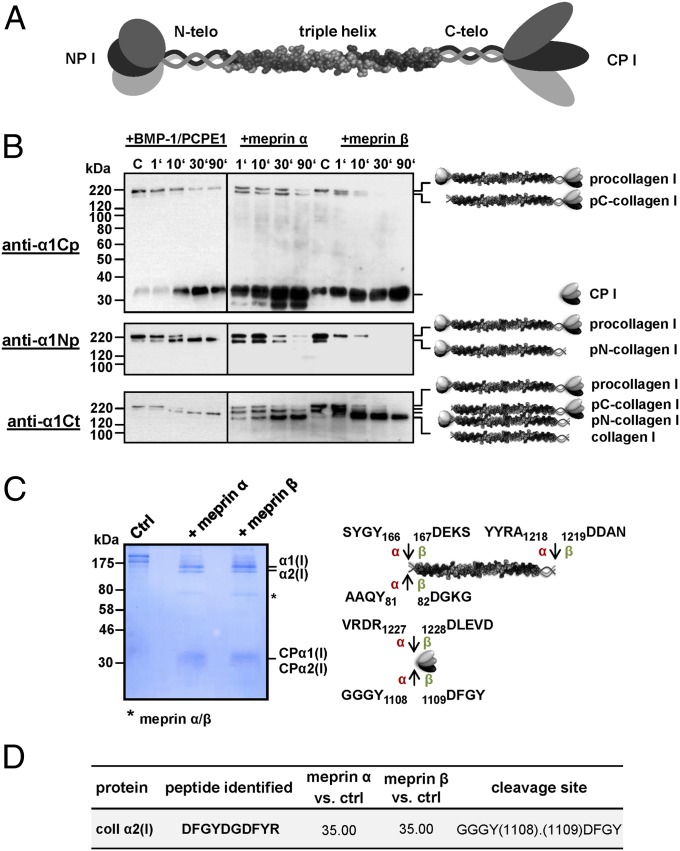
Fig. 1.
Cleavage of type I procollagen by meprin α and meprin β. (A) Schematic of the type I procollagen molecule consisting of an N-terminal propeptide (NP I), the N-telopeptide (N-telo), the triple helical region, the C-telopeptide (C-telo), and the C-terminal propeptide (CP I). (B) Cleavage of recombinant procollagen heterotrimer by BMP-1, meprin α, and meprin β. Here, 40 nM procollagen I was incubated with each 0.3 nM BMP-1 and PCPE-1 (40 nM), meprin α, or meprin β in a total volume of 50 µL for 1, 10, 30, and 90 min at 37 °C in assay buffer. Subsequently, samples were analyzed by SDS/PAGE (10% wt/vol polyacrylamide) under reducing conditions, followed by Western blotting using anti-collagen α1(I) C-propeptide antibody (anti-α1Cp), anti-collagen α1(I) N-propeptide antibody (anti-α1Np), and anti-collagen α1(I) C-telopeptide antibody (anti-α1Ct). Magic Mark XP (Invitrogen) was used for molecular weight markers. (C) Cleavage of procollagen I for proteomics analysis. Here, 170 μg/mL of recombinant procollagen I heterotrimer was processed with 50 nM meprin α or meprin β in a total volume of 30 µL, then analyzed by SDS/PAGE (10% wt/vol polyacrylamide), followed by staining with Coomassie blue. Arrows indicate cleavage sites analyzed by proteomics for meprin α (α) and meprin β (β). Numbers display positions of amino acids in the full-length protein. (D) C-terminal cleavage site in procollagen α2(I) identified by TAILS. Probability values were calculated with the iProphet algorithm, with high confidence in spectrum-to-peptide assignments. Abundance ratios of meprin α- or meprin β-treated cells vs. untreated control cells (ctrl) >15 identify meprin-generated neo-N-termini as high-confidence cleavage products. Sequences are given in one-letter code; detailed information is available elsewhere (36).