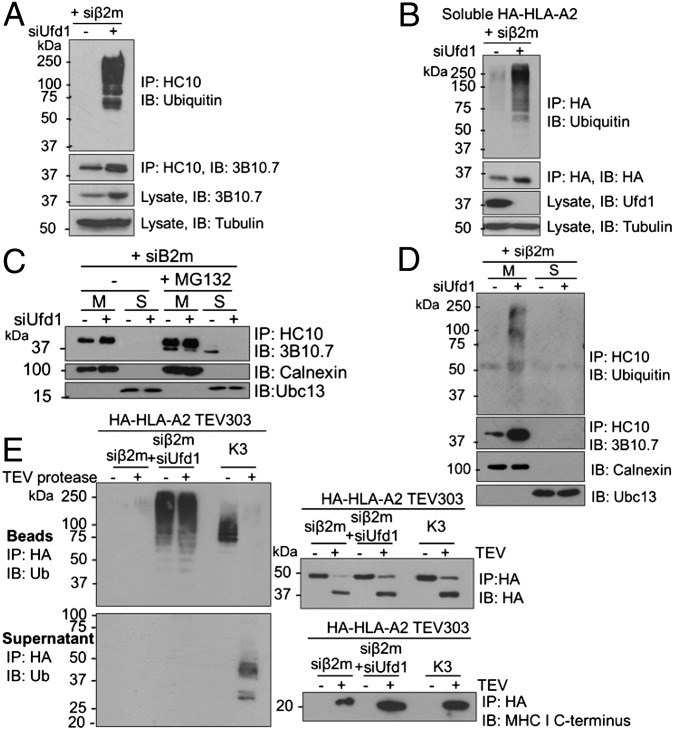
Fig. 4.
Ubiquitination of luminal MHC I residues precedes p97-mediated extraction from the ER membrane. (A and B) Ubiquitinated full-length and soluble MHC I HCs accumulate in the absence of a proteasome inhibitor on depletion of Ufd1. (A) Lysates from β2m siRNA-treated HeLa cells, treated with Ufd1 or control siRNA were immunoprecipitated with HC10 (MHC I) and probed for MHC I and ubiquitin. Lysates were directly probed for MHC I and tubulin control. (B) β2m-depleted cells expressing soluble HA-HLA-A2 treated with Ufd1 or control siRNA were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA and probed for ubiquitin and HA. (C and D) Ubiquitinated MHC I accumulates in the ER membrane in the absence of Ufd1. (C) β2m-depleted HeLa cells were treated with or without 50 μM MG132 for 5 h and fractionated into membrane (M) and soluble fractions (S). MHC I HCs were immunoprecipitated from each fraction and visualized with 3B10.7. On depletion of Ufd1, MHC I HC is retained in the membrane with no soluble, deglycosylated MHC I detected. Lysates were probed for calnexin and Ubc13 (fractionation controls). (D) Cells treated as in C. Immunoprecipitates additionally probed for ubiquitin. (E) Polyubiquitinated full-length MHC I HC stabilized on depletion of Ufd1 is ubiquitinated on ER luminal residues. Lysates from HA-HLA-A2 TEV303-expressing HeLa cells treated with β2m siRNA plus Ufd1 or control siRNA, or expressing K3 viral E3 ligase, were immunoprecipitated with anti–HA-agarose. On-bead incubation with TEV protease released the MHC I C terminus into the supernatant, and the residual HA-tagged N-terminal (luminal) fragment was eluted from the beads. Bead and supernatant fractions were probed for ubiquitin, HA, and MHC I C terminus.