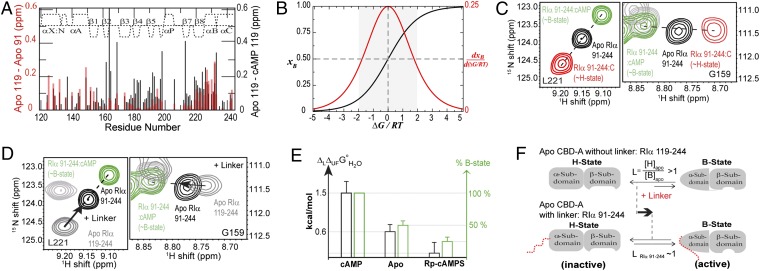
Fig. 2.
RIα (91-118) linker shifts the B vs. H equilibrium of apo CBD-A toward the B state. (A) apo RIα (119-244) vs. apo RIα (91-244) (red) and apo vs. cAMP-bound RIα (119-244) (black) chemical shift differences. (B) B-state molar fraction (xB) vs. ΔG/RT (black) computed for a two-state equilibrium, where ΔG = GH − GB. The red curve is the first derivative of xB vs. ΔG/RT. (C) Representative H–N correlation peaks for apo, cAMP-, and C-bound RIα (91-244). (D) As C with C-bound RIα (91-244) replaced by apo RIα (119-244). Arrows indicate the effect of linker addition on the H vs. B equilibrium. (E) Correlation between the percent of B state in CBD-A and ΔLΔUFGoH2O, which quantifies the strength of the linker–CBD interactions (Table S1). (F) Scheme for the linker-induced shift of the CBD-A H vs. B equilibrium.