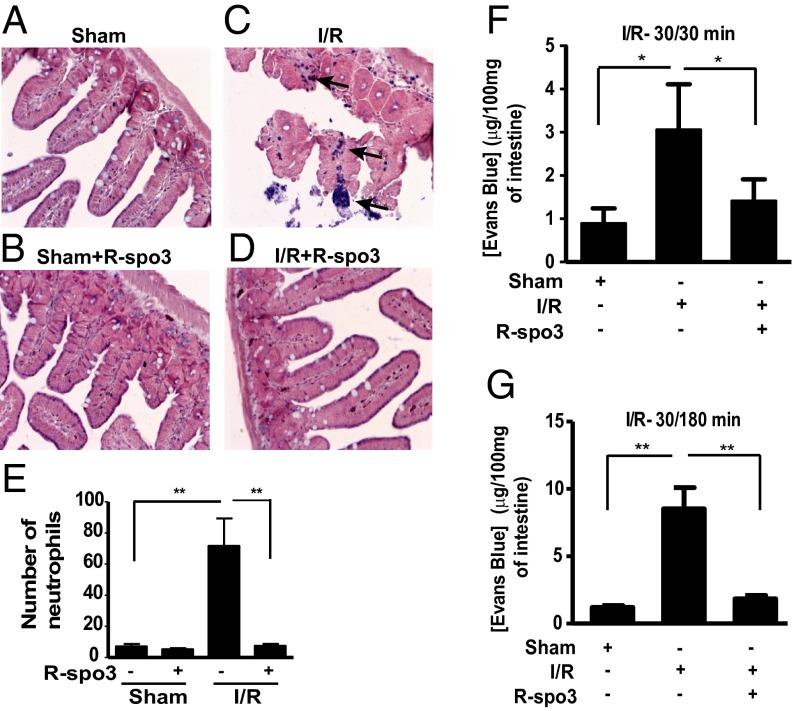
Fig. 4.
R-spo3 inhibits leukocyte infiltration and vascular leakage in the intestine. Influx of neutrophils to the site of damage was evaluated using naphthol AS-D choloroacetate substrate by esterase staining method. Representative images of intestinal sections, stained for neutrophils from groups (A) sham, (B) sham + R-spo3, (C) I/R, and (D) I/R + R-spo3 are shown. A lot of neutrophils were found in the interstitial spaces of the intestine in the I/R group as shown by the dark blue staining (arrows) and very few neutrophils were found in R-spo3–treated I/R mice. (E) Cumulative data on neutrophil numbers from each group (n = 9 per group, **P < 0.01). The extent of I/R for neutrophil staining is 30/180 min. Vascular leakage in the intestine was measured by extravasation of Evans blue dye at two different reperfusion time periods: 30/30 min I/R (F) and 30/180 min I/R (G) (n = 9 per group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). Mesenteric I/R-induced intestinal vascular leakage was significantly reduced in the intestine of R-spo3–treated I/R mice at both indicated time periods.