Figure 4.
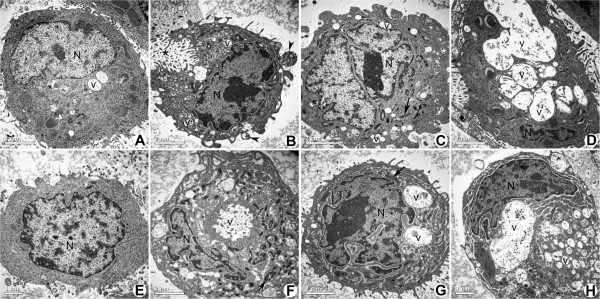
Electron micrographs comparing the effects of S. gratum, J. gangetica and L. flava on Kato-III (A-D) and NUGC-4 (E-H) 3 days post treatment. Scale bar 2 μm. A) Untreated Kato-III cell shows very few vesicles (v), a rather uniform rounded shape and chromatin scattered throughout nucleus (N). B) S. gratum treated Kato-III cell shows condensed chromatin in nucleus (N), apoptotic body formation (arrowhead) and many vesicles. The cell is dispersing as granular debris (*). C) Kato-III cell treated with J. gangetica. This cell shows chromatin condensation around the periphery of the nucleus, membrane bound organelles (arrow) and numerous vacuoles (v). D) Kato-III cell after exposure to L. flava shows a large number of autophagic vacuoles (v), and a shrinking nucleus (N) with condensed chromatin. E) Untreated NUGC-4 cell shows no condensation of chromatin in nucleus (N) and a rather uniform rounded shape. F) NUGC-4 cell treated with S. gratum shows chromatin condensation nucleus, numerous vesicles (v) and many membrane bound organelles (arrow). G) NUGC-4 cell after exposure to J. gangetica shows a nucleus condensed chromatin, membrane bound organelle (arrow) and vesicles (v). H) Morphological changes observed in L. flava treated NUGC-4 cell were comprised with chromatin condensation in the nucleus (N), and many heterogenous vesicles of varying size (v).
