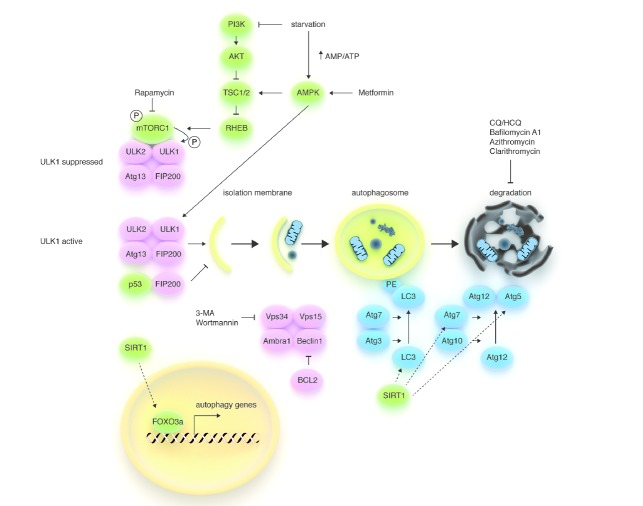
Figure 1.
Schematic model of the autophagic machinery. Autophagy starts with activation of the ULK1/2 kinase complex, which also includes ATG13 and FIP200. mTORC1, a protein complex that couples nutrient and growth factor availability to cell growth and division, inhibits the ULK1/2 complex by phosphorylating ULK1 on ‘negative’ sites. Conversely, AMPK (a sensor of energy store depletion that is also activated by metformin) activates the complex by directly phosphorylating (and consequently activating) ULK1 and by inhibiting mTORC1 (through phosphorylation of TSC1/2). Thus, the ULK complex becomes active during starvation, but can also be activated pharmacologically with rapamycin and its derivatives (i.e. sirolimus and everolimus) or with agents that directly or indirectly reduce PI3K signaling (i.e. TKIs in chronic myeloid leukemia). Phosphorylated and active ULK1 promotes phosphorylation of Atg13 and FIP200 and dissociates from mTORC1. The PI3K-III VPS34 is another hub for autophagosome formation, forming a protein complex together with UVRAG, AMBRA1, VPS15, and Beclin1. Atg8 (LC3)-PE and the Atg12/Atg5 conjugation systems, which execute the lipid modification of LC3-I, leading to LC3-II-PE binding to the autophagosomal membrane, complete autophagosome formation. Autophagosomes’ content, such as proteins and organelles, is readily digested upon their fusion with lysosomes. The antiapoptotic protein BCL2 prevents the assembly of the Beclin1 interactome by interacting with Beclin1 through its BH3 domain, while the NAD+-dependent deacetylase SIRT1 promotes autophagy by enhancing FOXO3a-dependent transcription of autophagy genes and by directly deacetylating Atg proteins. VPS34 inhibitors, such as 3-MA and wortmannin, are effective at inhibiting the early stages of autophagy, while Bafilomycin A1, CQ, HCQ, and macrolides, such as clarithromycin, block autophagy at later stages by preventing the fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes.